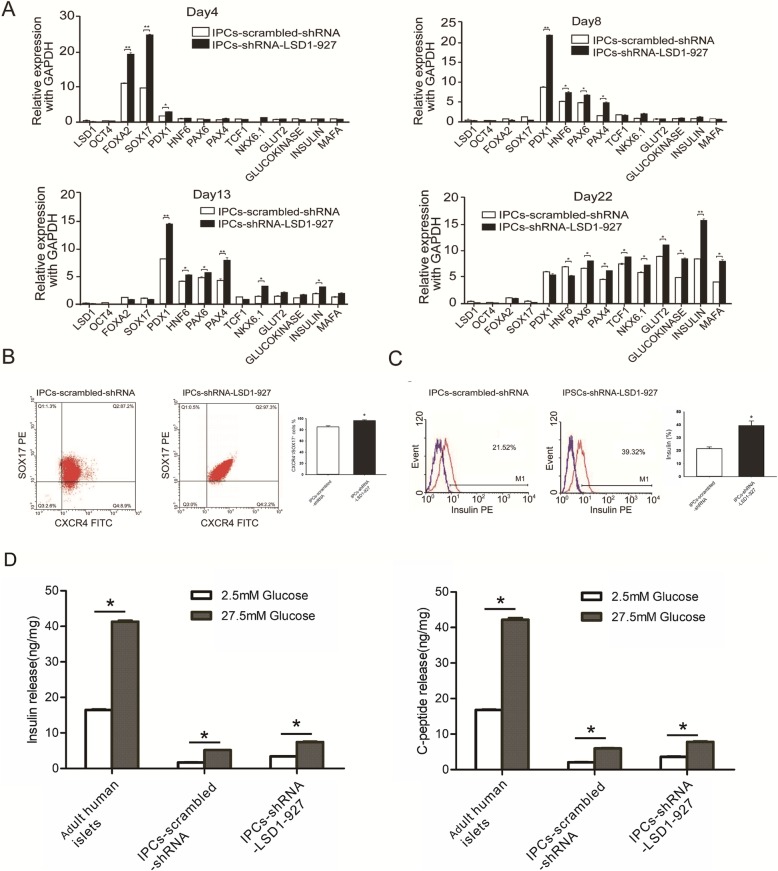
Fig. 2.
Functional characteristics in the pancreatic β cells derived from hiPSCs at the final maturation stage. a Gene expression of pancreas-related developmental genes during hiPSC differentiation to IPCs (n = 3). b Flow cytometry analysis of differentiated hiPSCs revealed that after stage 1, 96.3% ± 1.54% of the cells with shRNA-LSD1-927 were SOX17+ and CXCR4+ double-positive, and 85.06% ± 2.14% of the control cells (scrambled-shRNA) were double-positive. A significant difference was observed between the two groups (*P < 0.05, n = 3). c Flow cytometry analysis revealed that IPCs at the final maturation stage derived from hiPSCs-shRNA-LSD-927 were 38.32% ± 3.54% and those derived from hiPSCs-scrambled-shRNA were 20.42% ± 1.36%. A significant difference was found between the two groups (*P < 0.05, n = 3). d Differentiated IPCs release insulin and C-peptide (n = 3). Glucose-induced insulin release data correspond to the amount of insulin and C-peptide secreted for 1 h after 2.5 and 27.5 mM glucose stimulation