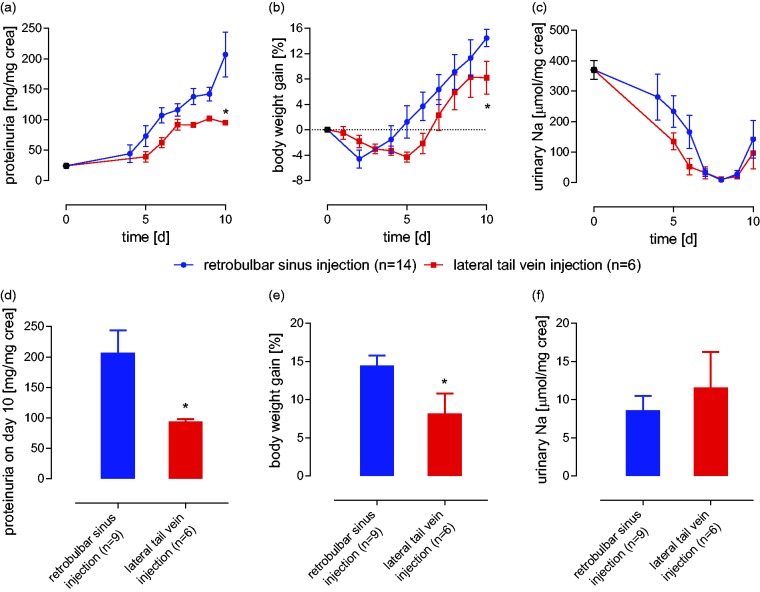
Figure 3.
Course of experimental nephrotic syndrome after doxorubicin injections via tail vein v. retrobulbar sinus injections in mice exhibiting a response. Following retrobulbar sinus injections of doxorubicin, all the hallmarks of human nephrotic syndrome were present. This included (a) proteinuria, (b) body weight gain, and (c) urinary sodium retention. Following the lateral tail vein injections, the maximal proteinuria (D) and body weight gain (E) were less pronounced, and the minimal sodium excretion (F) was higher. (* indicates a significant difference between retrobulbar sinus injection and lateral tail vein injection (based on Student’s t-test and the Mann-Whitney U-test, as appropriate.)