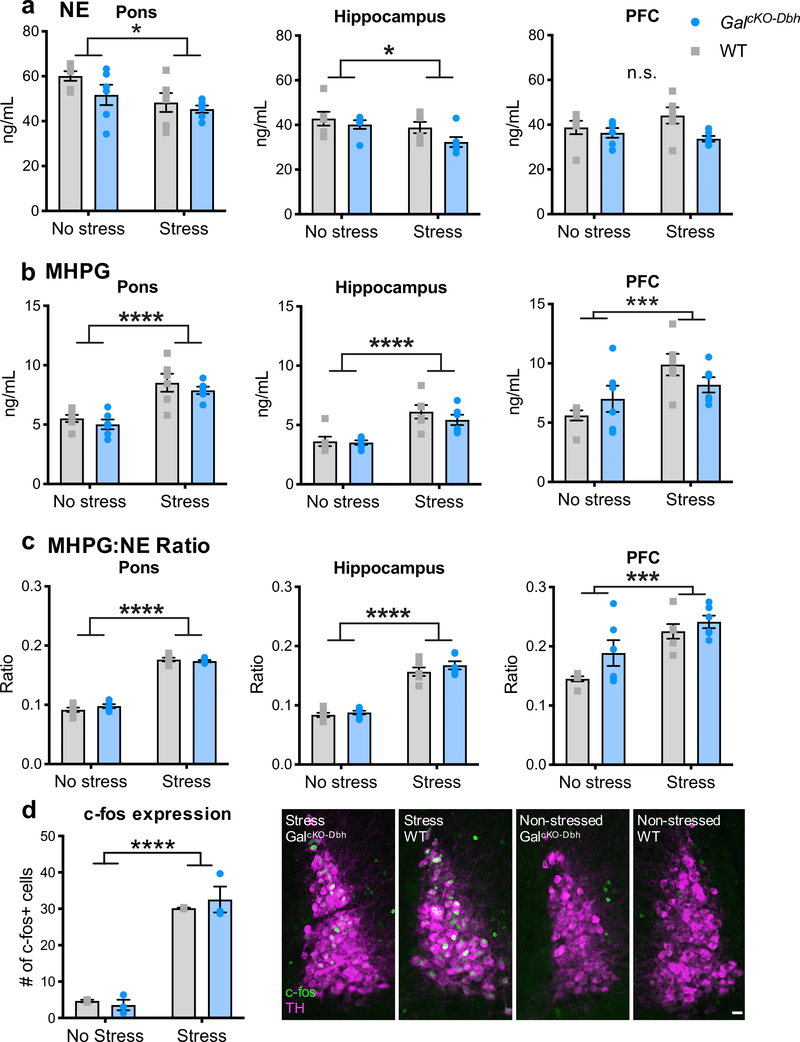
Figure 7. Baseline and stress-induced NE turnover and LC c-fos expression are normal in GalcKO-Dbh mice.
NE (a) and the major metabolite of NE, MHPG (b), were measured via HPLC at baseline and after acute foot shock stress in the pons, hippocampus, and PFC. Foot shock stress caused an overall decrease in NE and increase in MHPG, leading to an increase in the MHPG:NE ratio in all three brain regions. No differences were seen between genotypes in either the raw measurements or the MHPG:NE ratio. n = 6 mice per group. Fos immunohistochemistry and quantification did not show any differences between GalcKO-Dbh mice and WT littermate control mice at baseline or after acute restraint stress (d) Right. Representative LC sections stained for Fos (antibody; green) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH antibody; magenta). n = 3 slices per animal, 2–3 animals per group. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA. Scale bar, 20 μm. Error bars show SEM. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, n.s., non-significant.