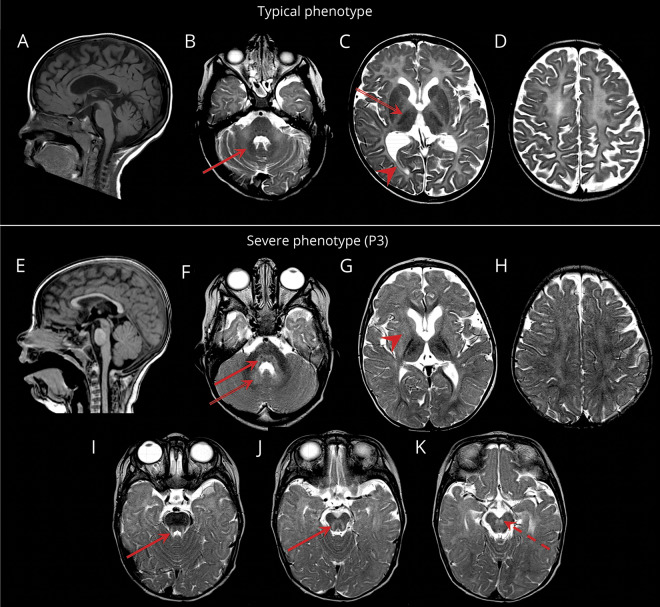
Figure 1. MRI characteristics.
Sagittal T1-weighted (A, E) and axial T2-weighted (B–D, F–K) images. (A–D) Typical POLR3-HLD; MRI obtained at age 6 years. Hypomyelination with relative preservation (T2 hypointensity) of the dentate nucleus (red arrow; B), anterolateral nucleus of the thalamus (double-lined arrow; C), optic radiations (arrowhead; C), globus pallidus, and corticospinal tracts in the posterior limb of the internal capsule (not shown). Thinning of the corpus callosum and cerebellar atrophy are also seen. (E–K) Severe phenotype; MRI of patient 3 obtained at age 10 months. Mild insufficient myelin deposition, not meeting the criteria for diffuse hypomyelination. Loss of myelin (T2 hyperintensity) in the posterior brainstem (red arrows; F, I, J), red nucleus (red dashed arrow; K), and hilus of the dentate nucleus (double-lined arrow; F). Abnormal signal of the lentiform nucleus (arrowhead; G). Supratentorial atrophy (G–H) and diffuse atrophy of the basal ganglia and thalami (G) are also seen.