Table 1.
Overview of parameter assumptions for the model
| Parameter | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|
| R 0, basic reproduction number | Central 95% range is 1.4–3.9 Gamma distributed, 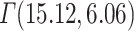
|
Li et al.10 |
| λ 0, rate of arrival of infected travellers (individuals per week) at time when interventions are introduced | 0.1, 1, or 10 or 100 | Assumption |
| θ, probability that infected traveller is not detected by screening | Exit screening only: 46% (95% CI: 37%, 57%) Entry and exit screening: 42% (95% CI: 33%, 53%) No screening: 100% (100%, 100%) | Quilty et al.6 |
| ρ, effectiveness of traveller sensitisation | 0%, 25%, Sensitivity analyses: 50% | Gostic et al., Hellewell et al.5,8 |
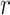 , epidemic growth rate (per day) , epidemic growth rate (per day) |
Central 95% range is 0.05–0.16 Gamma distributed, 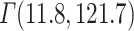
|
Li et al.10 |
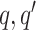 , probability of outbreak caused by a single infected traveller (without and with intervention, respectively) , probability of outbreak caused by a single infected traveller (without and with intervention, respectively) |
Solution to Equation 1 with 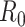 for for 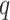 and and 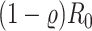 for for 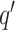
|
Hartfield and Alizon16 |
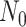 , number of infected arrivals required to trigger an outbreak in absence of interventions , number of infected arrivals required to trigger an outbreak in absence of interventions |
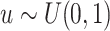 quantile of a geometric distribution with probability quantile of a geometric distribution with probability 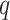
|
Derived |
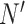 , number of infected arrivals required to trigger an outbreak in presence of interventions , number of infected arrivals required to trigger an outbreak in presence of interventions |
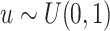 quantile (matched to above) of a geometric distribution with probability quantile (matched to above) of a geometric distribution with probability 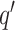
|
Derived |
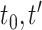 , arrival time for the infected traveller who triggers an outbreak, without and with interventions , arrival time for the infected traveller who triggers an outbreak, without and with interventions |
Poisson process with intensity 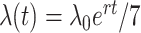
|
Derived |
| k, dispersion parameter for number of secondary infections | 0.54 Sensitivity analyses: 0.1 and 2.00 (influenza-like) | Riou and Althaus, Lloyd-Smith et al., Endo et al.20,22,23 |
