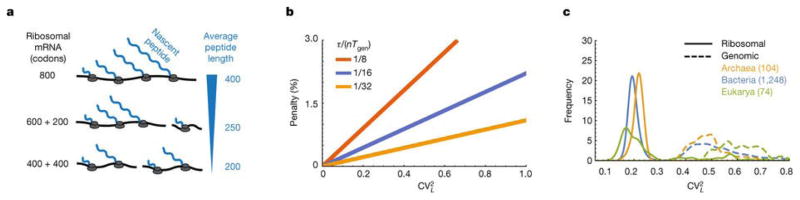
Figure 3.
A. Dividing up a long r-protein (e.g. 8oo codons) into two unequal parts (600 and 200 codons) does not reduce the average length of the nascent peptides as much as dividing it into equal parts (400 and 400 codons). B. The minimal time fraction that ribosomes must spend on their own production from Eq. 3, normalized by n(2τ/nTgen −1) from Eq. 1 and plotted as a function of for different values of τ/nTgen (1/8 red, 1/16 blue, 1/32 yellow) to show the percentage penalty that results from CVL > 0. C. Relative frequencies of the normalized variance ( from Eq. 3) of protein length distributions in ribosomes and genomes, showing substantially lower CV s for the former.