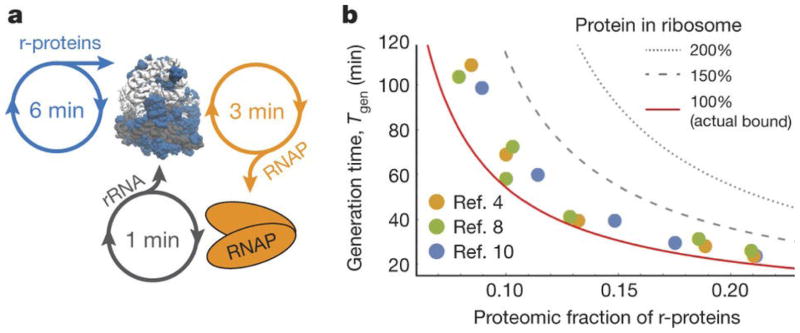
Figure 4.
A. Ribosome auto-production occupies ribosome time to make r-proteins and RNA polymerases for rRNA production. An RNA polymerase can be translated in half the time compared to a set of r-proteins, and in fast-growing E. coli, each polymerase can produce 20 sets of rRNAs per generation. B. Generation time vs. proteomic fraction of E. coli r-proteins. Circles are published experimental data: yellow [4], green [8], and blue[10]. Because most proteins in E. coli are stable, the proteomic fraction of r-proteins roughly equals the fraction of time, ϕ, ribosomes spend translating r-proteins. The solid line is the bound on generation time set by ribosome production, Tgen ≥ τln(2)/ϕ (rearranged Eq. 1 in high n limit). For the same ribosome speed, cells with hypothetical ribosomes replacing rRNA mass for r-protein (e.g., 150% or 200% the actual amount) could not divide as quickly.