Fig. 5. Mechanism of the treatments, RBCM-Algae decrease the protein level of HIF1α and VEGF and promotes cell apoptosis and necrosis.
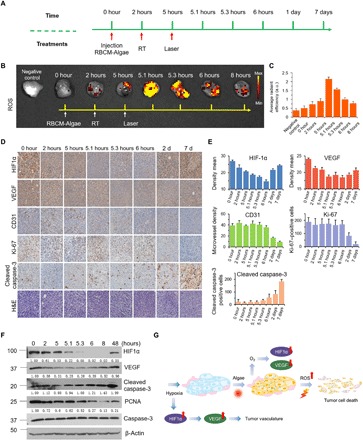
(A) Tumor collection timetable from the process of in vivo anticancer PBS biosystem therapy. (B) Bioluminescence imaging and (C) the corresponding quantitative analysis of tumor tissues that were stained with ROS probe (DCFH). (D) Representative HIF1α, CD31, Ki-67, cleaved caspase-3, and H&E staining of tumor section from in situ 4T1 tumor–bearing mice of RBCM-Algae treated by RBCM-Algae + RT + laser and the corresponding immunohistochemical index quantitative analysis (E). (F) Immunoblotting of HIF1α, VEGF, cleaved caspase-3, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and caspase-3 protein level from 4T1 tumor–bearing mice of the RBCM-Algae + RT + laser group and the corresponding quantitative analysis. (G) Possible mechanism of the RBCM-Algae–mediated combination therapy. Data are means ± SD, n = 3.
