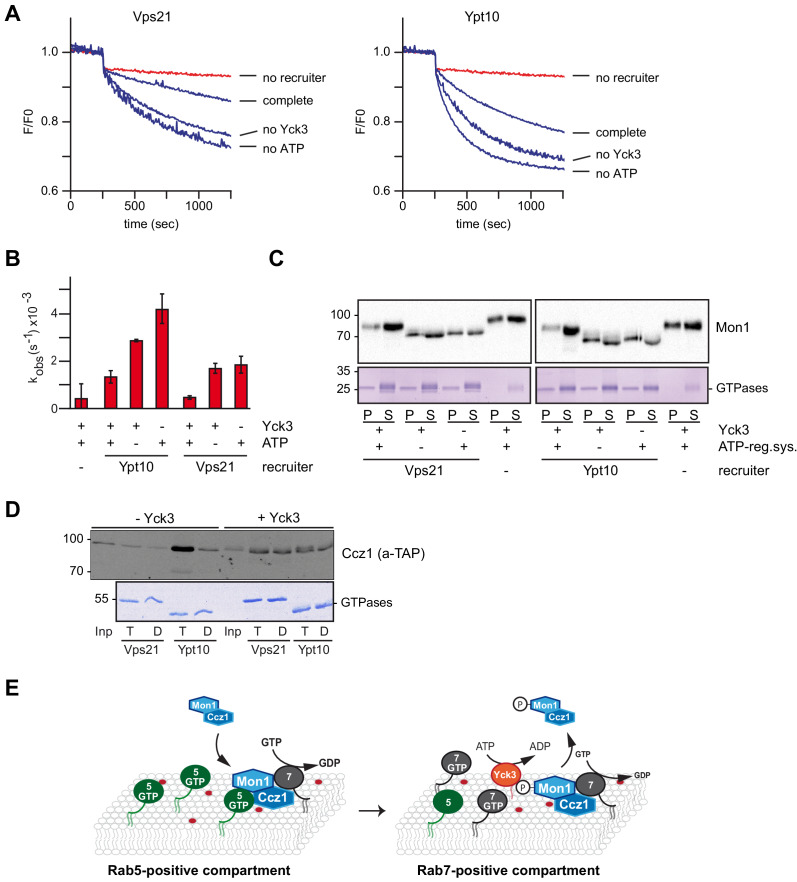
Figure 6. The casein kinase Yck3 regulates interaction of Rab5 with Mon1-Ccz1 in yeast.
(A) Recruiter GEF-assay of phosphorylated Mon1-Ccz1. 50 nM Mon1-Ccz1 were pretreated either with Yck3 and ATP (complete) or with either one of them (no Yck3/no ATP) before it was used in the recruiter GEF assay as described in Figure 3A. 1.5 µM GTP-loaded pVps21 or pYpt10 were used as a recruiter GTPase, as control proteoliposomes were mock treated (no recruiter). (B) Rate constants as calculated from (A). Error bars represent standard deviation. (C) Soluble and membrane fraction of recruiter assays in (A) were recovered and separated by centrifugation for 20 min at 20,000 g, 4°C. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western-Blot for presence of Mon1, and by Coomassie staining for used Rab-GTPases. (D) Interaction of yeast Rab5-like proteins with Mon1-Ccz1. Purified GST-tagged Rab5 proteins (Vps21, Ypt10) were loaded with GTP (T) or GDP (D) and incubated with purified Yck3 or mock-treated Mon1-Ccz1 complex. Eluates were analyzed on SDS-PAGE by Western blotting with an antibody against the TAP-tag on Ccz1 (top) and by Coomassie staining (bottom). For details see methods. (E) Working model. Mon1-Ccz1 is recruited to charged membranes. On a Rab5-positive compartment, where Mon1-Ccz1 interacts with Rab5, its GEF-activity towards Rab7 is stimulated. This would lead to a fast transition from a Rab5 to a Rab7-positive compartment. The Rab7-positive compartment converts from an endosomal to a lysosomal/vacuolar membrane. After fusion with the lysosome-like vacuole in yeast, Mon1-Ccz1 is phosphorylated by Yck3. This abolishes the interaction with Rab5 and may in addition lead to a release of Mon1-Ccz1 from the vacuole (Lawrence et al., 2014).
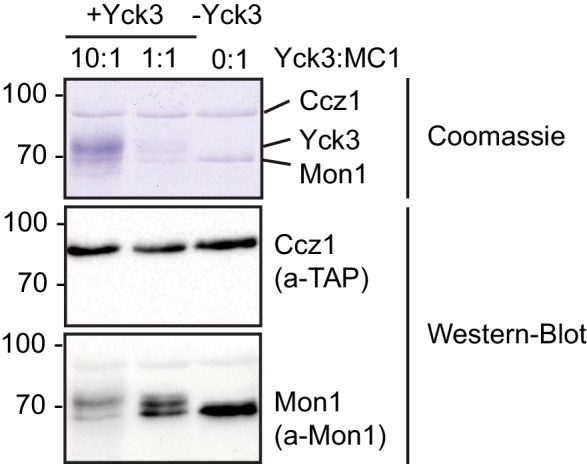
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Phosphorylation of yeast Mon1-Cz1 by Yck3 in vitro.