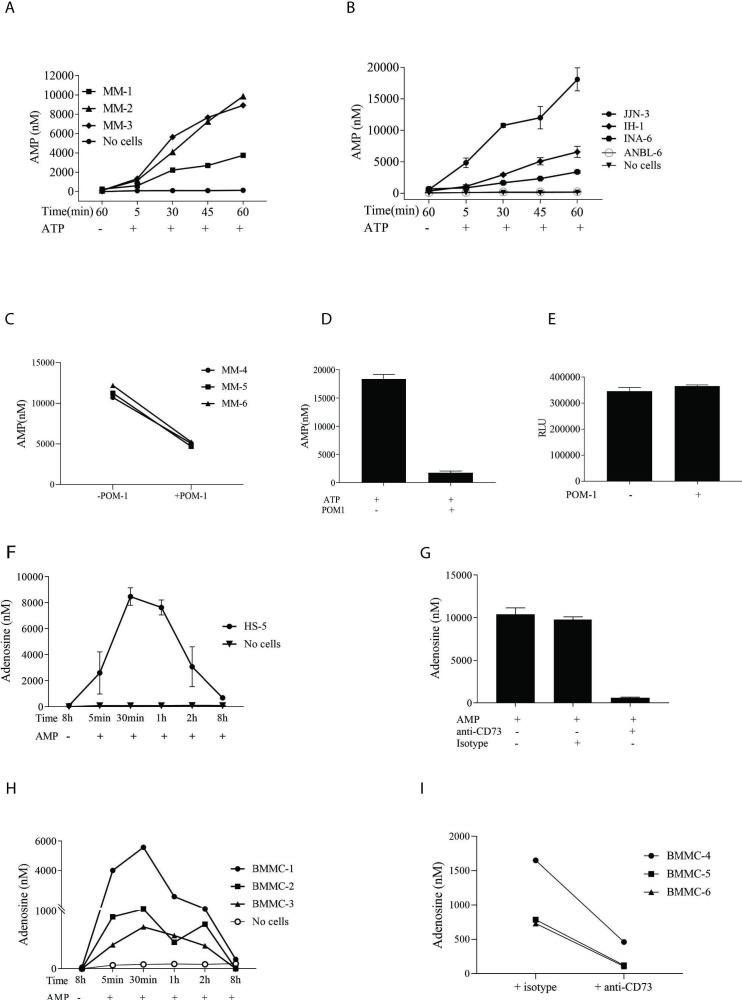
Figure 2.
Production and inhibition of AMP and adenosine by cells from MM patients and HMCLs using anti-CD73 and POM-1. CD138+ MM cells enriched from BM aspirate from three patients (>95% purity); MM (1–3) (A) and 4 HMCLs (B) were incubated with 100 µM ATP for indicated time periods before collection of supernatants for measurement of AMP by HPLC-MS. Figure shows mean±SD. (C) POM-1 (100 µM) inhibited AMP generation by primary MM (4–6) cells and (D) by JJN-3. Cells were incubated with or without 100 µM POM-1 for 3 hours and cultured with 100 µM ATP for 1 hour. (E) POM-1 did not reduce intracellular ATP level, an indirect measurement of cell death, in JJN-3 cells. Cell viability was measured by CTG cell viability assay. Human BM stromal/stem cell line (HS-5) (F) and BMMC from 3 MM patients (H) were incubated with 100 µM AMP for various time periods before collection of supernatants for HPLC-MS. (G) 150 µg/mL anti-CD73 or isotype controls were used to inhibit adenosine generation by HS-5 cell line and by BMMC from 3 MM patients (I). B, D, E, F, and G show one representative out of three independent experiments. BM, bone marrow; BMMC, BMmononuclear cells; CTG, CellTiter-Glo luminescent; HMCL, myeloma cell lines; MM, multiple myeloma.