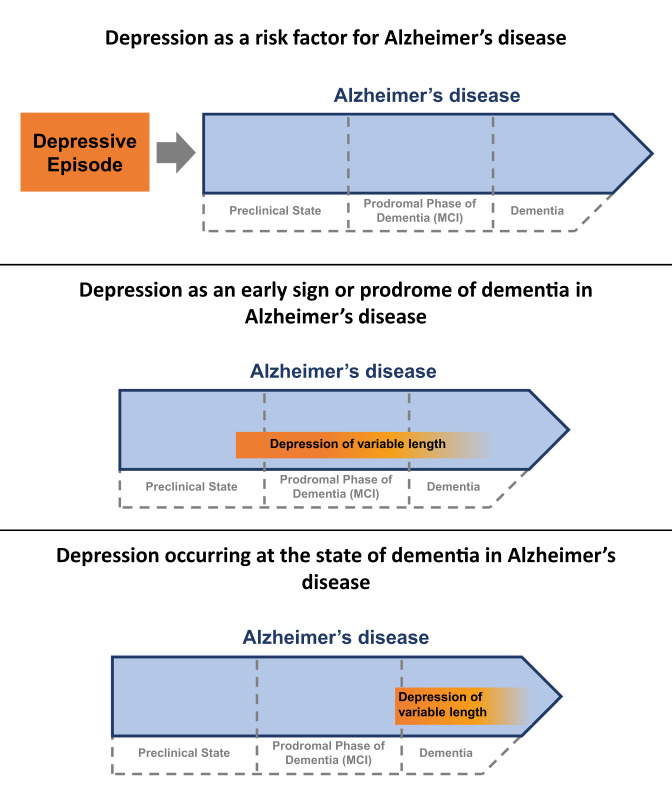
Fig. 1. The relationship between depression and cognitive decline throughout the development and clinical course of Alzheimer‘s disease (AD).
Depression can occur in three different stages in relation to the process of neurodegeneration in AD. Depression can be a predisposing risk factor occuring before the onset of AD pathology. It might also be an early sign of neurodegenerative changes or a prodromal symptom with or without cognitive deficits. Finally, it may occur at the more advanced dementia stage of AD. In every stage depression is an important accelerating factor contributing to the clinical progression and conversion from a preclinical state to MCI and to dementia.