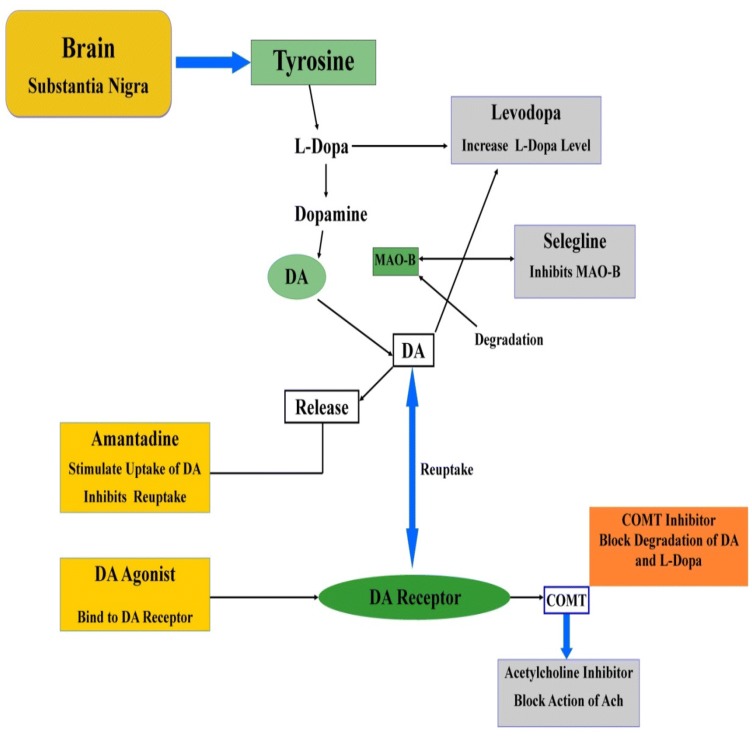
Fig. 3.
Metabolic pathway of l-dopa agent against Parkinson’s disease. Degeneration of the substantia nigra occurs in patients with Parkinson's disease. l-Dopa is converted to dopamine with the help of enzyme DPOPA decarboxylase. This happens both in thecentral nervous system and within the peripheral circulation after levodopa has crossed the blood–brain barrier. Once converted to dopamine, it activates postsynaptic dopaminergic receptors and compensates for the decrease in endogenous dopamine. (MAO-B inhibitors decrease DA levels,which can ensure its rapid breakdown by the catalytic enzyme monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B), whose level is increased within the Parkinson's disease. Selegiline is well tolerated used MAO-B inhibitor, which, when administered with l-DOPA, may sustain the response of l-DOPA. Dopamine agonists can increase DA levels within the brain and are most active during the early stages of Parkinson's disease. They will even be combined with l-DOPA in the late stages of Parkinson's disease to extend the lifetime of l-DOPA). l-DOPA L-3, 4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, DA dopamine, DA Agonist dopamine agonist, MAO-B monoamine oxidase B, COMT catechol-O-methyltransferase, Ach acetylcholine.