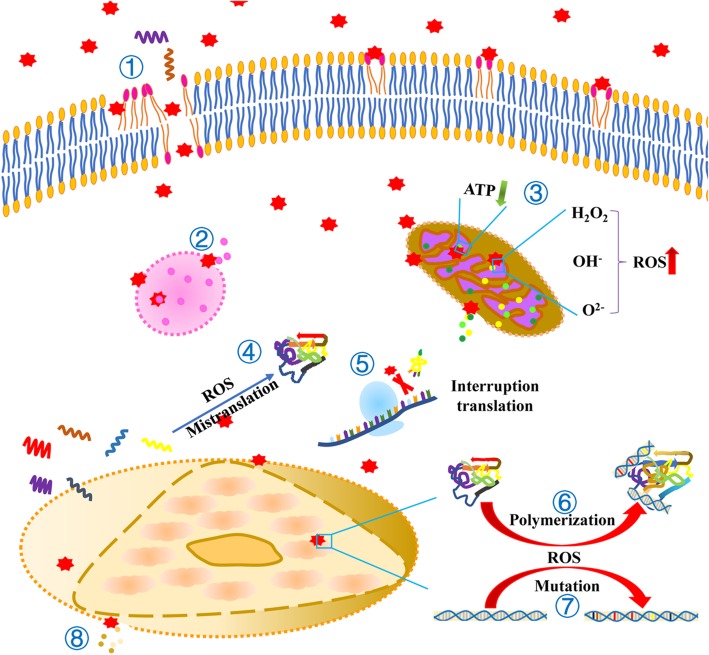
Fig. 3.
Cellular events induced by NPs. ① NPs contribute to the destruction of the cell membrane and to lipid peroxidation. ② The lysosomal membrane is destroyed by NPs and results in the release of their contents. ③ The mitochondrial membrane is damaged by NPs, leading to content release. NPs reduce the generation of ATP and increase the production of ROS. ④ The ROS induced by NPs results in the mistranslation of RNA. ⑤ NPs prevent the binding of tRNA to the ribosome. ⑥ The ROS induced by NPs result in the polymerization of proteins and DNA. ⑦ The ROS induced by NPs leads to DNA mutations ⑧ The nuclear membrane is destroyed by NPs, resulting in the release of its contents