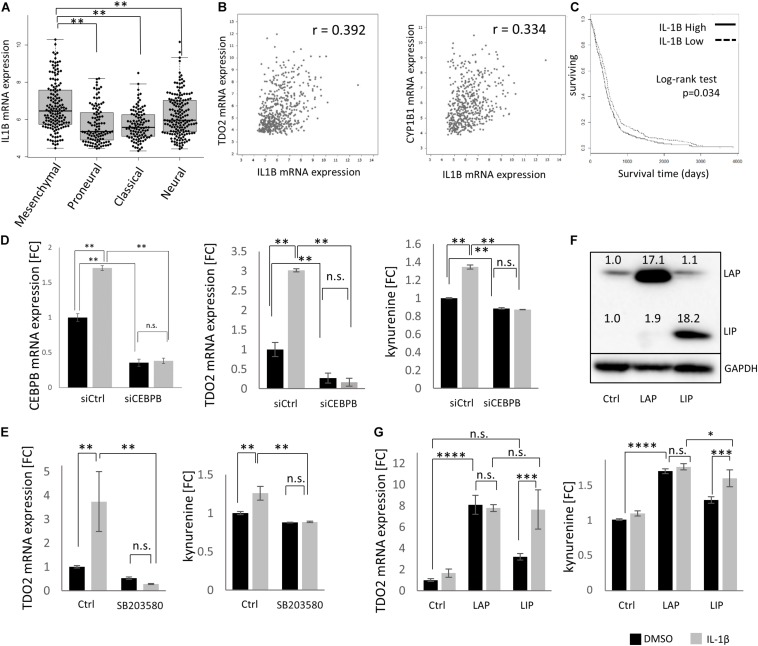
FIGURE 3.
IL1B drives CEBPB expression in glioblastoma (GBM). (A) mRNA expression of IL1B in different GBM subtypes within The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA dataset. (B) mRNA expression of IL1B correlated with TDO2 (left) and CYP1B1 (right) in GBM samples. (C) Kaplan–Meier analysis of overall survival of GBM patients according to the expression of IL1B (log-rank p = 0.034, high n = 263, low n = 262). (D) siRNA-mediated knockdown of CEBPB in T98G cells results in a decrease of CEBPB mRNA levels, as well as a decrease in TDO2 mRNA expression and concomitant kynurenine (Kyn) levels. (E) The CEBPB-driven increase in TDO2 expression (left) and Kyn levels (right) mediated by IL-1β treatment is blocked by the MAPK inhibitor SB203580. (F) Stably transfected T98G cells overexpressing CEBPB LIP or LAP isoforms show higher levels of the respective CEBPβ protein isoform. (G) TDO2 mRNA expression (left) and Kyn production (right) in T98G cells overexpressing CEBPB LAP or LIP in response to IL-1β treatment. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001.