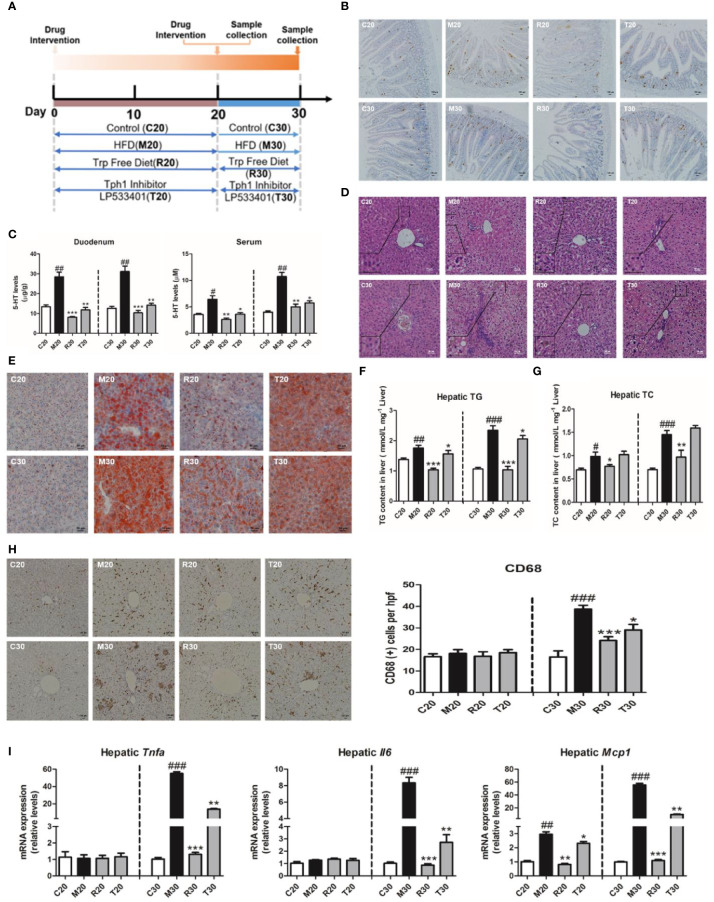
Figure 2.
Gut-derived serotonin (GDS) deficiency ameliorated the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). (A) Experimental procedure. (B) The content of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) positive cell in duodenum of SD rats. (C) The content of 5-HT in serum and duodenum of SD rats. (D) Hematoxylin–eosin (H&E) staining results of each group of rats (evaluated by 6 experts, ×200). (E) Oil red O staining (small red circle) shows hepatic lipid deposits (×200). Hepatic TG concentrations (F) and TC concentrations (G) in SD rats. (H) The CD68 positive cells content (×100). (I) The messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of genes related to the inflammatory response (Tnfα, Il6, Mcp1) in SD rats fed an HFSD diet on days 20 and 30. The terms C20, C30, and M20, etc., are explained in Animals and Treatments. All data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 6). ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, compared with corresponding control group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with relative model group.