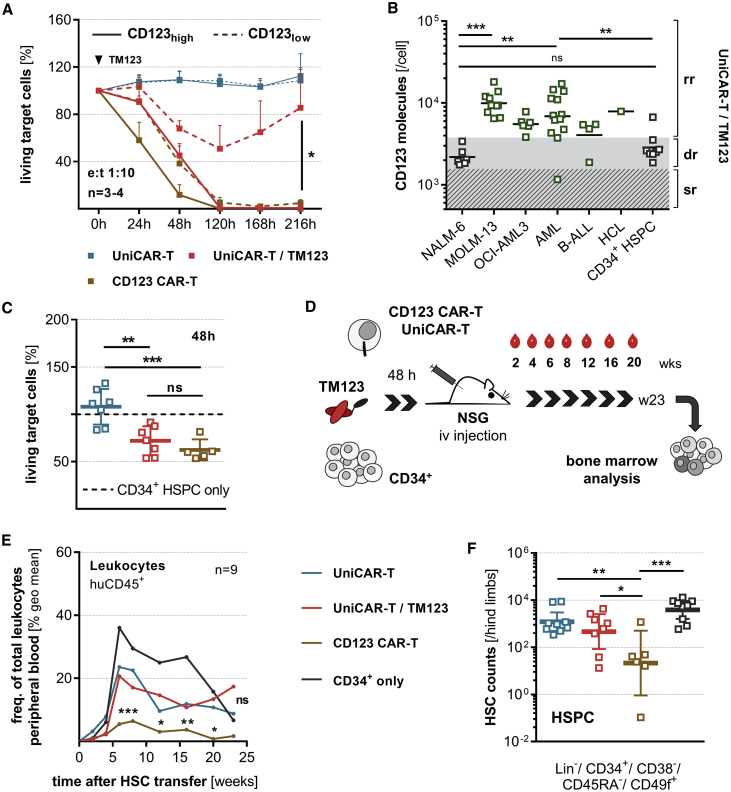
Figure 6.
Hematotoxic Effects of Constitutively Active CD123 CAR-T in Humanized Mice Are Prevented By the Switch-Off Mechanism of UniCAR-T
(A) UniCAR-T or CD123 CAR-T (2 × 103) were incubated with 1:1 pre-mixed CD123high- and CD123low-expressing cells (OCI-AML3, NALM-6) at an e:t ratio of 1:10. TM123 was added once at the start of the experiment in the respective groups. Long-term cytotoxic responses against individual target cell populations were monitored for 216 h (mean ± SEM). (B) CD123 was quantified via an antigen standard curve on cell lines, patient-derived leukemia samples, and CD34-purified hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) from granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)-mobilized healthy donors. Rapid (rr), delayed (dr), and slow response (sr) ranges of UniCAR-T with TM123 have been adapted to pre-determined anti-tumor efficacy rates against several CD123-expressing cell lines. (C) CD34+ HSPCs purified from G-CSF-mobilized healthy donors were co-cultured with allogeneic CD123 CAR-T or UniCAR-T with or without 5 nM TM123 at an e:t ratio of 1:2. Cytotoxic response against hematopoietic progenitors was determined after 48 h of incubation of CD34+ HSPCs (1 × 105) with CAR-T (5 × 104). Results were normalized to control samples containing CD34+ progenitors only. (D) Mixtures of CD34+ HSPCs (1 × 106) and CD123 CAR-T or UniCAR-T (5 × 105) combined with or without 5 nM TM123 cultured for 48 h were subsequently injected into sub-lethally irradiated NSG mice. Peripheral blood (PB) samples were taken up to 20 weeks after transplantation. (E) Engraftment analysis of CD45+ human leukocytes within PB. Significance levels were calculated relative to the control group injected with CD34+ cells only. (F) Bone marrow (BM) samples were analyzed for the presence of the lineage marker negative compartment (Lin−) and in particular for the hematopoietic stem cell-enriched cell pool via flow cytometry 23 weeks after transplantation (geometric mean ± 95% confidence interval [CI]). For analysis of human cell engraftment for all individual mice, see also Figure S5D. Statistical significance was assessed by a parametric one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s (A and B) or Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (C and F) and nonparametric ANOVA (Kruskal-Wallis test) with a post hoc Dunn’s multiple comparison test (E) (∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001).