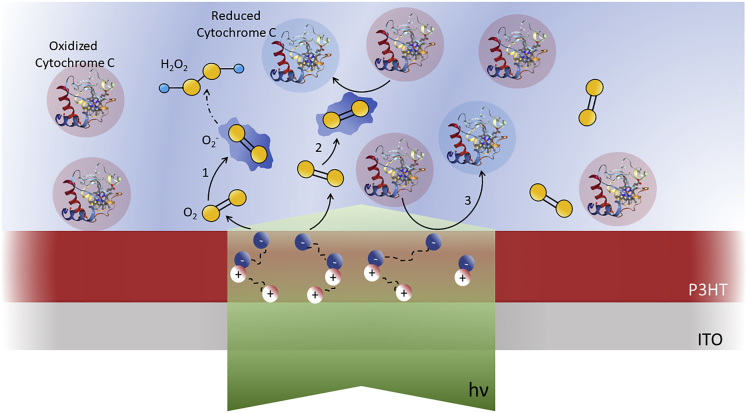
Figure 5.
Photocatalysis of P3HT Actively Regulates CytC Redox State Both through Direct- and Oxygen-Mediated Electron Transfer
Sketch of polymer-mediated, light-triggered electrochemical reactions occurring at the hybrid solid-liquid interface between rr-P3HT, CytC, and PB electrolyte solution. Light (green shaded area) impinges on the polymer thin film from bottom ITO side and generates polaron states, which undergo fast dissociation processes into free charges. Electrons predominantly migrate toward electrolyte interface and allow electron transfer reactions. Three photoelectrochemical reactions are observed: (1) interaction with oxygen dissolved in the aqueous electrolyte (yellow), superoxide formation, and subsequent hydrogen peroxide formation; (2) superoxide formation and subsequent CytC reduction (represented as red-blue transition of the CytC protein); (3) direct interaction between P3HT charged states and CytC(III).