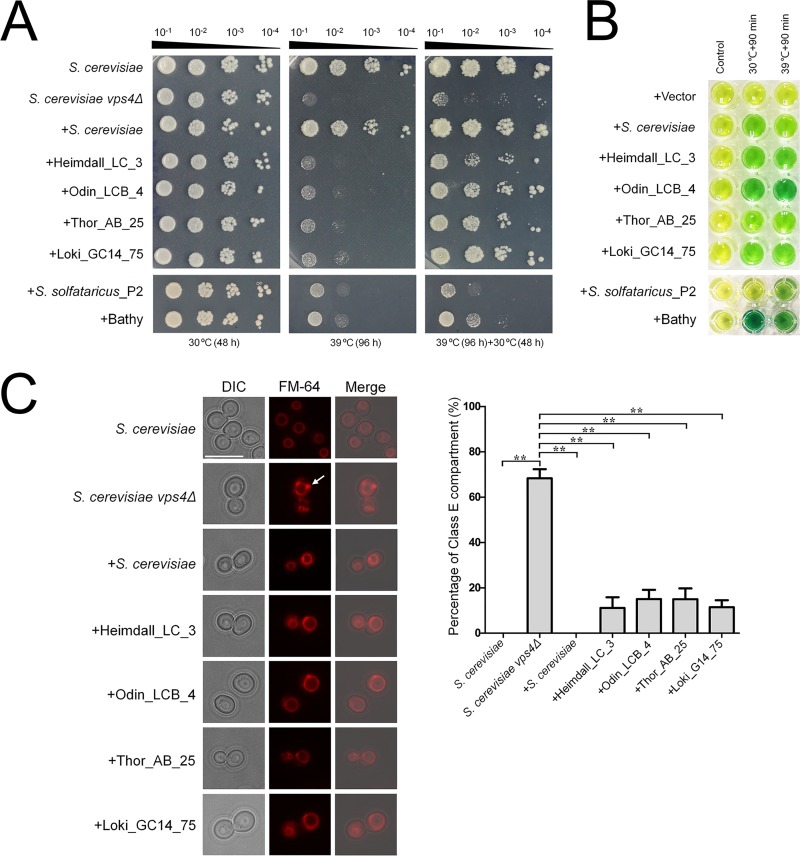
FIG 4.
Functional complementation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae vps4 null mutants by Asgard Vps4. (A) Complementation of the high-temperature-sensitive growth defect of vps4 mutant cells. Five microliters of a series of 10-fold dilutions derived from a starting suspension of an OD600 of 10−1 was inoculated into SC-Ura medium. (B) The ATPase activity of S. cerevisiae Vps4, Asgard Vps4, and Cdvs at 30°C and 39°C were confirmed by a malachite green assay. The substrates would turn from golden to green owing to the inorganic phosphate released from ATP hydrolysis by Vps4 under the indicated condition. (C, left) The class E compartments in S. cerevisiae vps4 null mutants were largely abrogated by Asgard Vps4. The vacuolar morphologies in the indicated strains were visualized by fluorescence microscopy. The white arrow indicates the class E compartment in a vps4 null mutant. Bar = 10 μm. (Right) Quantification of class E compartment in the indicated strains. The results represented the means from three independent replicates (20 cells per experiment), and standard deviations are indicated by the error bars. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison test. **, P < 0.01.