Figure 4.
Protein Levels of Enzymes Involved in Glycogen Metabolism Are Selectively Reduced after Reperfusion in a Mouse Stroke Model
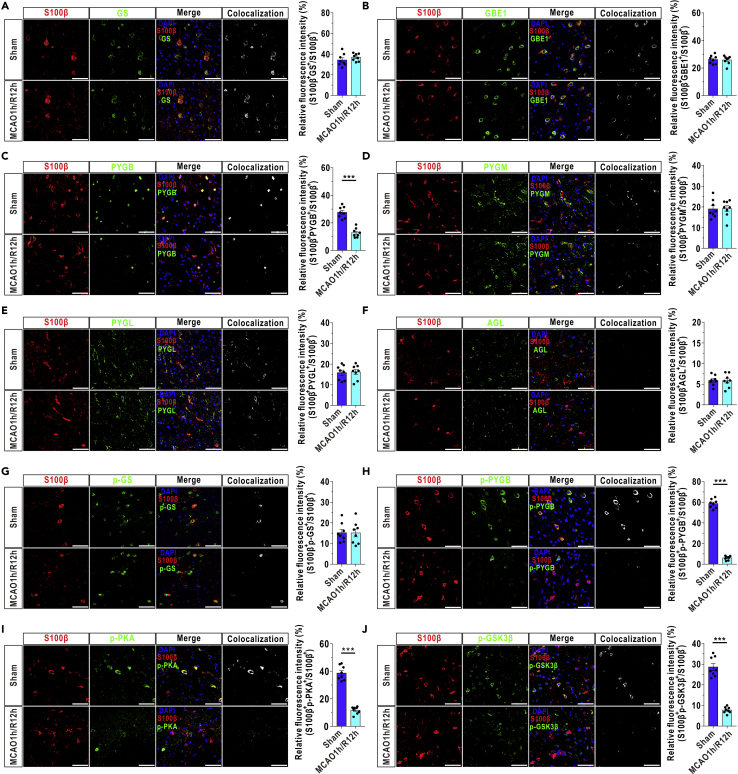
(A–F) Left panels: coronal immunofluorescence images of frontal cortex area 1 in the ischemic penumbra after staining with an antibody against S100β and antibodies against GS (A), GBE1 (B), PYGB (C), PYGM (D), PYGL (E), and AGL (F). Right panels: quantification of relative fluorescence intensity of GS (A), GBE1 (B), PYGB (C), PYGM (D), PYGL (E), and AGL (F) in astrocytes of the ischemic penumbra at 12 h after reperfusion (n = 8, independent t test). Astrocytes were marked with S100β. The relative fluorescence intensity of the target protein was calculated as the percentage of fluorescence intensity in the colocalization area (denoted as S100β and target protein) divided by the fluorescence intensity in the S100β+ area. Scale bars represent 50 μm.
(G–J) Left panels: coronal immunofluorescence images of frontal cortex area 1 in the ischemic penumbra after staining with an antibody against S100β and antibodies against phosphorylated GS (p-GS, G), phosphorylated PYGB (p-PYGB, H), phosphorylated PKA (p-PKA, I) and phosphorylated GSK3β (p-GSK3β, J). Right panels: quantification of relative fluorescence intensity of p-GS (G), p-PYGB (H), p-PKA (I), and p-GSK3β (J) in astrocytes of the ischemic penumbra at 12 h after reperfusion (n = 8, independent ttest). Astrocytes were marked with S100β. Scale bars represent 50 μm.
The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S3, S4, and S13 and Table S2.