Figure 10.
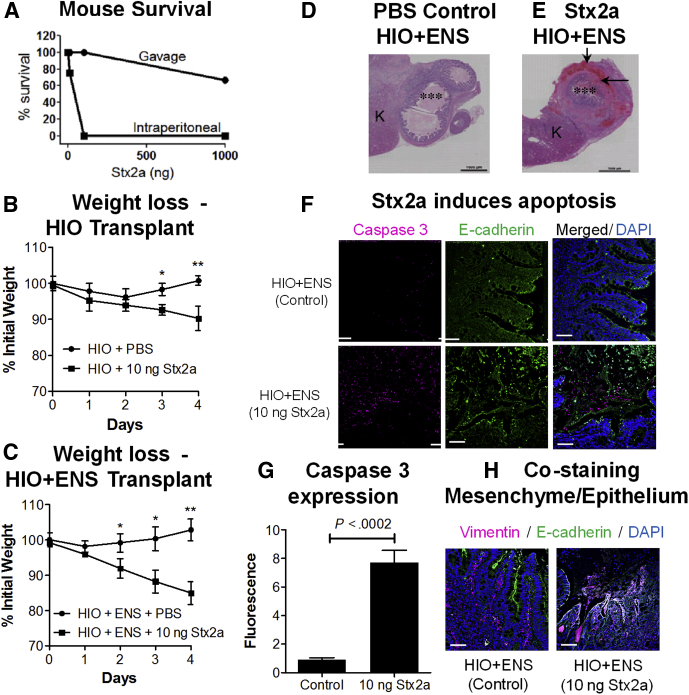
Modeling human responses to Stx in vivo in mice. (A) Susceptibility of mice to Stx2a is dependent on mode of delivery. Mice were challenged with 10, 100, or 1000 ng of Stx2a delivered orally by gavage (3 mice per group) or by IP injection (4 mice per group), and viability was followed up for 5 days. (B and C) Injection of Stx2a into transplanted human organoids causes weight loss in vivo. HIOs transplanted under the kidney capsule of NSG mice were injected with PBS or Stx2a (10 ng). Mice were weighed daily, and the mean percentage of initial weight is plotted ± SEM, n = 3. Statistically significant difference in weight, control vs Stx2a-treated on same day, ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01 by 2-tailed unpaired t test. (B) Stx2a injection into HIO transplants. (C) Stx2a injection into HIO + ENS transplants. (D and E) Stained sections of mouse HIO + ENS transplants. Transplants were injected with PBS or Stx2a, harvested on day 4, and stained with H&E. ∗∗∗Injected lumen. Black arrows, regions of damage. Representative images of experiments performed in triplicate. (D) PBS-injected HIO + ENS. (E) Stx2a-injected (10 ng) HIO + ENS. (F) Stx2a induces apoptosis in HIO + ENS transplants. Sections of control (top) and Stx2a challenged HIO + ENS (bottom) kidneys stained for apoptotic marker caspase 3 (red), E-cadherin (green), and DNA (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole [DAPI], blue). Scale bar: 50 μm. (G) Quantification of caspase 3. Fluorescence intensity was quantified using ImageJ software, and plotted as means ± SD, n = 3. Statistical significance was assessed using a 2-tailed, unpaired t test. (H) Co-staining for mesenchymal and epithelial markers. Sections of control or Stx2a-challenged HIO + ENS kidneys were stained for vimentin (red) to identify mesenchymal cells, E-cadherin (green) to identify epithelial cells, and DNA (DAPI). Co-staining for E-cadherin and vimentin (yellow) was seen in HIO + ENS challenged with Stx2a. Scale bar: 50 μm. K, kidney.