Fig. 1.
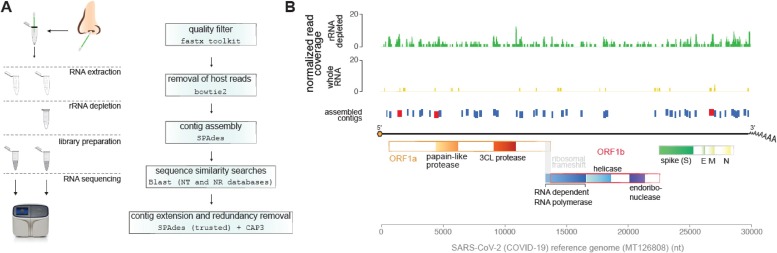
Identification of SARS-Cov-2 through nasopharyngeal swab metatranscriptomics. A) Left panel: extraction of RNA from nasopharyngeal swab was performed according to a protocol validated in our laboratory (COVID-19 Extraction and Amplification with Maxwell® 16 Viral Total Nucleic Acid and GoTaq® Probe 1-Step RT-qPCR; Application Report, Promega 2020). Total RNA sequencing after rRNA depletion followed the protocol of the Ion Total RNA-Seq kit v2, in the Ion S5 platform. Depletion of human ribosomal RNA was done with the Low Input RiboMinus™ Eukaryote System v2 kit. Right panel: raw reads were submitted to quality filter where reads larger than 30 nt with Phred quality > 20 were aligned into human reference genome. Unaligned reads were used to perform contig assemblage. Assembled contigs were compared to NCBI databases using Blast software. Contigs that presented sequence similarity to SARS-Cov2-2 with e-value lower than 1e-5 were considered as from viral origin. Viral contigs were further submitted to contig extension using SPAdes and ‘trusted contigs’ option that was followed by cap3 tool to remove sequence redundancy. B) SARS-Cov-2 coverage profile of reads and assembled contigs. Reads were normalized by number of reads from each library. Contigs in red indicate high quality contigs larger than 400 nt with coverage of reads in both libraries.