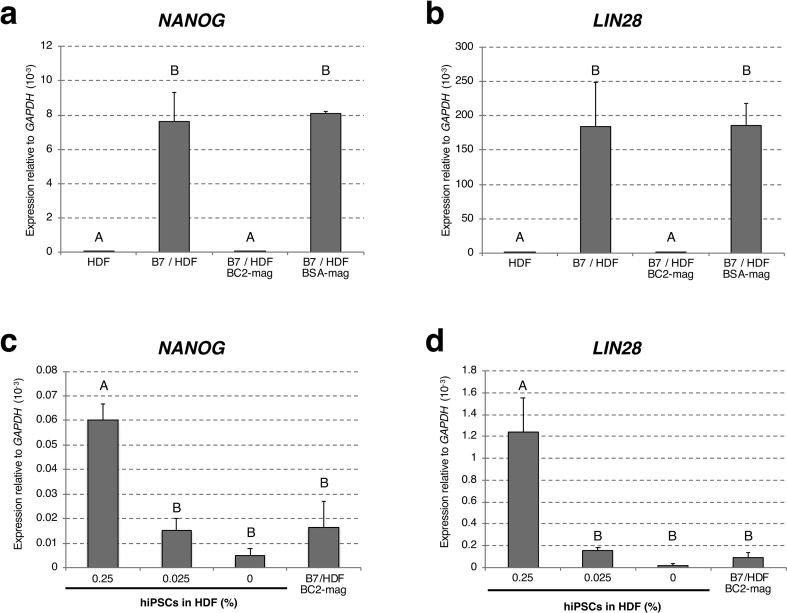
Fig. 3.
Detection of hiPSCs by droplet digital RT-PCR. Droplet digital PCR analysis to estimate residual hiPSC frequency after magnetic cell separation by rBC2LCN was performed by evaluating the expression of pluripotent stem cell marker genes, NANOG (a, c) and LIN28 (b, d). After mixing 1 × 106 of iPSCs and HDF at a ratio of 1: 1 respectively, negative-sorted cells by rBC2LCN-magnetic beads were analysed (a–d) Absolute counts were normalised to GAPDH (per 1000 copies of GAPDH). Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation of independent triplicate experiments (n = 3). Data were analysed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's HSD test (a, b) The relative copy numbers of NANOG (a) and LIN28 (b) mRNAs in 50 ng of total RNA derived from magnetically sorted or unsorted cell mixtures. Significant differences are represented by different letters (Fig. 3a: p < 0.001; Fig. 3b: p < 0.005) (c, d) Relative copy number comparison between NANOG (c) and LIN28 (d) mRNAs in 50 ng of total RNA derived from magnetically sorted cell mixtures, and comparison samples in which HDF-derived total RNA was spiked with hiPSC-derived total RNA at a ratio of 0, 0.025%, or 0.25% by weight. There are significant differences between different letters (p < 0.001). B7: human iPS cell line 201B7. BC2-mag: rBC2LCN-magnetic beads. BSA-mag: BSA-magnetic beads.