FIGURE 4.
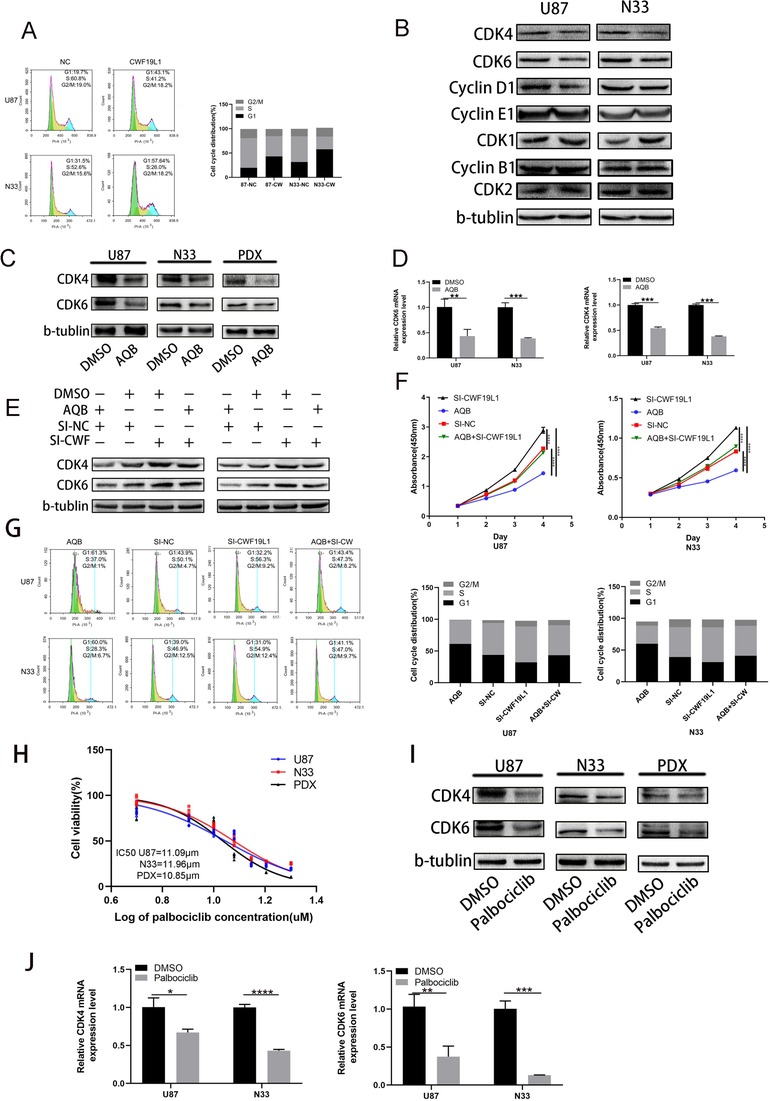
The significant role of CWF19L1 in the cell cycle of glioma. A, The flow cytometry analysis of the cell cycle stages of U87 and N33 cells transfected with the CWF19L1 plasmid and NC group plasmid. B, After 48 hours of U87 and N33 cell overexpression of the CWF19L1 plasmid, the western blot of CDK1, CDK2, cyclinE1, and cyclinB1 did not significantly change, when compared with the NC group. The CDK4, CDK6, and cyclinD1 expression decreased, with β‐actin as a loading control. C and D, The qPCR and western blot data of CDK4 and CDK6 expression in glioma cells after treatment with AQB. E and F, The rescue experiment by adding SI‐CWF19L1 in the presence or absence of AQB in glioma cells, the western blot analysis of CDK4 and CDK6 expression in U87 and N33 cells, the cell viability of U87 and N33 cells transfected with SI‐CWF19L1, and the use of AQB separately or combined were detected using by CCK‐8 assay. G, The flow cycle analysis of the cell cycle distribution of glioma cells. H, The IC50 of CDK4/CDK6 inhibitor palbociclib. I and J, The qPCR and western blot data revealed the CDK4 and CDK6 expression in glioma cells at 2 days after AQB treatment (* P < .05, ** P < .01, *** P < .001, **** P < .0001)
