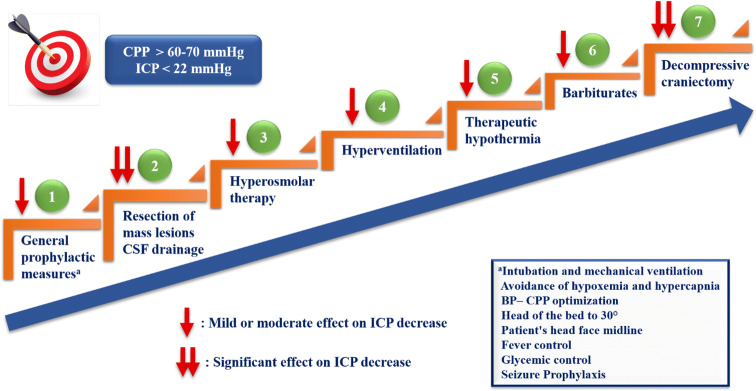
Fig. 3.
Staircase therapeutic approach of intracranial hypertension. An optimal therapeutic strategy is considered the step-by-step escalation of available interventions [29, 129], tailored for each patient. The primary goal is to maintain ICP below 22 mmHg and CPP above 60 mmHg [3]. Initially, general prophylactic measures should be applied immediately to all patients with suspected IH. Based on specific indications and conditions, surgical resection of mass lesions [48] and CSF drainage [3, 48, 69] should be considered as an initial treatment for lowering ICP. The following steps in turn include hyperosmolar therapy (mannitol or hypertonic saline) [3], which represents the cornerstone of medical treatment of acute IH, hyperventilation and therapeutic hypothermia [107, 108]. Τo control elevated ICP refractory to maximum standard medical and surgical treatment, at first, high-dose barbiturate administration [3] and then decompressive craniectomy [3, 48, 69] as a last step are recommended. This staircase therapeutic approach is based mainly on clinical experience rather than on strong published evidence. ICP: Intracranial pressure, CPP: Cerebral pressure perfusion, IH: Intracranial hypertension, CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid, BP: Blood pressure