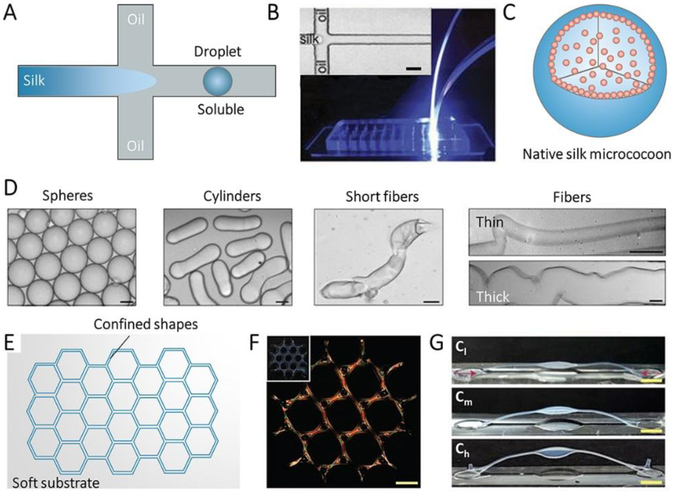
Figure 6.
Confined self-assembly of SF. A, Illustration of microfluidic device for confined self-assembly of SF with oil/water interface. B, Photograph of the microfluidic device, the inset is optical microscopy images of the fluid channel in the microfluidic device. Scale bar, 20 mm. C, Illustration of the sphere assembled with SF by the microfluidic device. D, Bright field microscopy images of various SF micrococoons. Scale bar, 5 mm. Reproduced with permission.[32] Copyright 2017, Springer-Nature. E, Illustration of a groove on a soft substrate with the confined shape. F, Polarization microscopy image of large-scale structures of silk fibrils composed of tri-hexagonal components. Inset: Camera images of the whole structure taken under the diffuse white light. Scale bars, 1 mm. G, Buckling of high-aspect-ratio beams with increasing birefringence/alignment of fibers induced via contraction. Cl, Cm, and Ch indicate samples respectively with low (10–25%), medium (25–40%) and high (>40%) contraction. Reproduced with permission. [37] Copyright 2017, Springer-Nature.