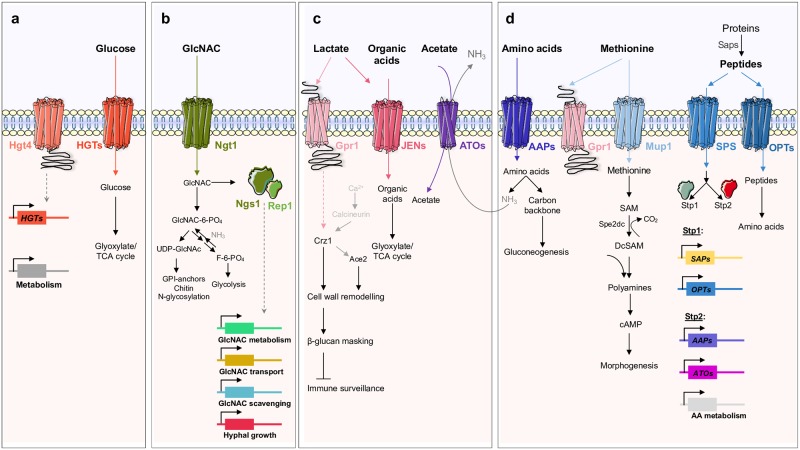
Fig 2. Schematic representation of the main sensing, transport, and transduction systems for the utilization of different host nutrients in Candida species.
(a) In C. albicans, glucose is sensed by Hgt4, generating an intracellular signal that induces the expression of HGTs and other metabolic genes. (b) In C. albicans and C. tropicalis, the uptake of GlcNAc occurs through the Ngt1 transporter. (c) The uptake of carboxylic acids is facilitated by the Jen (in C. albicans) and Ato transporters (in C. albicans and C. glabrata). In C. albicans, Gpr1 is reported to be a lactate and methionine sensor. In the presence of lactate, Gpr1 is thought to activate Crz1 in a calcineurin-independent manner and, together with Ace2, regulates a polygenic response that leads to β-glucan masking. (d) Peptides and amino acids are sensed by the SPS complex, which induces the expression of Opts, Aaps, and Ato transporters, as well as SAPs and amino acid catabolic genes. Intracellular ammonia resulting from the catabolism of GlcNAc or amino acids is exported via Ato transporters. In the presence of methionine, and in low glucose conditions, the methionine-induced morphogenesis is activated via Gpr1 sensor and Mup1 transporter. AA, amino acid; Aap, amino acid permease; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; DcSAM, decarboxylated S-adenosylmethionine; GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine; GPI, glycosylphosphatidylinositol; HGT, hexose transporter; Opt, oligopeptide transporter; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; SAP, secretory aspartyl proteinase; SPS, Ssy1-Ptr3-SSy5; Sp2DC, Sp2 decarboxylase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; UDP, uridine diphosphate.