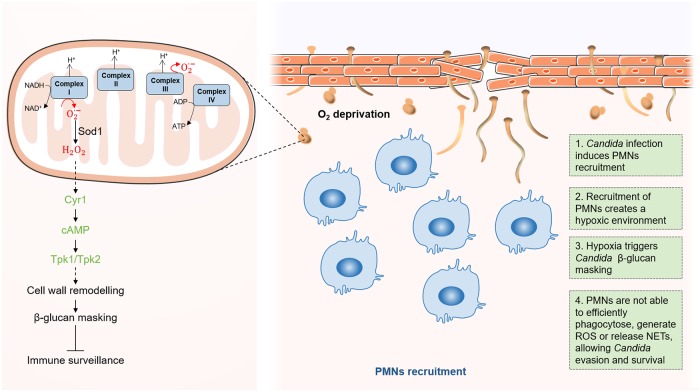
Fig 4. Candida adaptation to hypoxic host niches.
During C. albicans infections, the recruitment of PMNs creates an hypoxic environment [88]. In the fungus, this oxygen limitation triggers increased formation of ROS, such as superoxide (O2•−), from the electron transport chain [98,99]. Superoxide is then converted into diffusible hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by the action of Sod1. H2O2 has been proposed to activate adenylyl cyclase (Cyr1) and cAMP-PKA (Tpk1/2) signaling, which in turn triggers cell-wall remodeling and β-glucan masking [97]. This β-glucan masking allows the fungus to evade phagocytosis by the PMNs [88]. cAMP, cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate; NET, neutrophil extracellular trap; PKA, Protein Kinase A; PMN, polymorphonuclear leukocyte; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Sod1, superoxide dismutase 1.