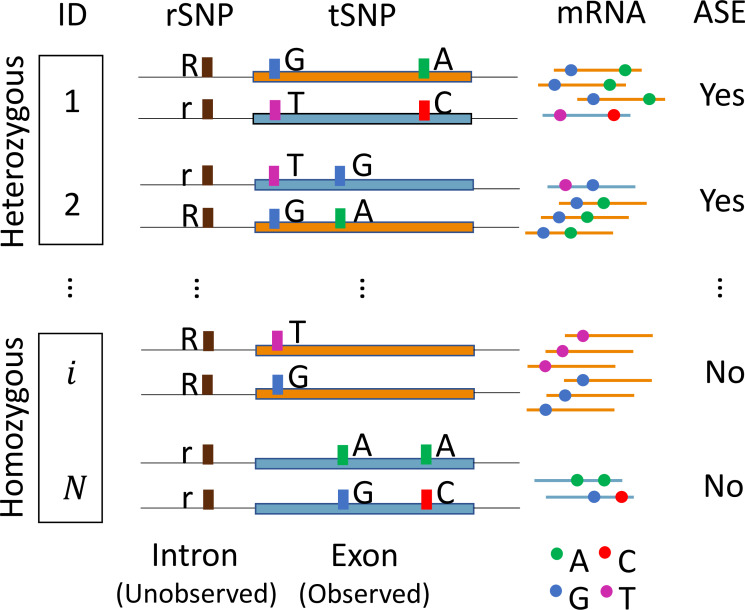
Fig 1. Challenges in cross-individual gene-based ASE analysis.
Heterogeneity of the ASE effect exists across individuals in a population. Because the cis-regulatory SNP (rSNP) is often unobserved, the bulk RNA-seq data include individuals (ID) that are either heterozygous or homozygous at the rSNP. The mRNA expression levels differ between two haplotypes only in those heterozygous individuals. Additionally, a gene may have multiple heterozygous transcribed SNPs (tSNPs). To differentiate paternal and maternal alleles, haplotype phase information is needed, which is often not available in most studies. Further complicating the analysis, to aggregate ASE effects across individuals, haplotypes that reside on the same allele of the unobserved rSNP need to be aligned across individuals.