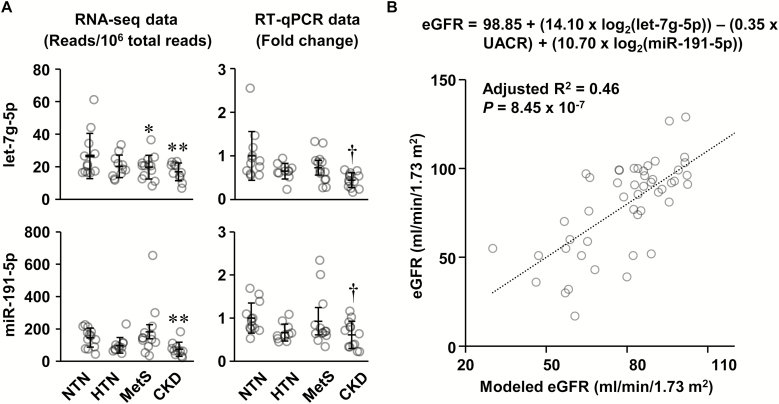
Figure 1.
Circulating let-7g-5p and miR-191-5p are decreased in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients, and let-7g-5p, miR-191-5p, and urinary albumin/creatinine ratio (UACR) are independent predictors of the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). (a) Two of the top 11 most abundant differentially expressed microRNAs were validated by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data are presented in the left panels and the RT-qPCR data in the right panels. Means ± SD and individual value of the normotensive subjects (NTN), and patients with hypertension (HTN) associated or not with other features of the metabolic syndrome (MetS) or with CKD are presented, n = 13–15 for RNA-seq data and 12–14 for RT-qPCR data. The geometric mean of miR-92b-3p, let-7f-5p, and miR-126-5p was used for normalization of RT-qPCR results. RNA-seq data were analyzed using an analysis of variance (ANOVA) one-way like test in EdgeR based on generalized linear models with a threshold of false discovery rate (q) <0.1. RT-qPCR log2 fold change data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by a Student–Newman–Keuls post hoc test with a threshold of P < 0.05. *q < 0.1, **q < 0.05, and †P < 0.05 vs. NTN. (b) Stepwise multiple linear regression was used to determine the best model to predict the eGFR using the let-7g-5p and miR-191-5p log2 fold change determined by RT-qPCR and clinical parameters (age, UACR, carotid distensibility, neutrophil and lymphocyte fractions, neutrophil number, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio) that are correlated with eGFR. The best model of 3 is shown that included let-7g-5p (P = 0.001), UACR (P = 0.006), and miR-191-5p (P = 0.014). n = 49.