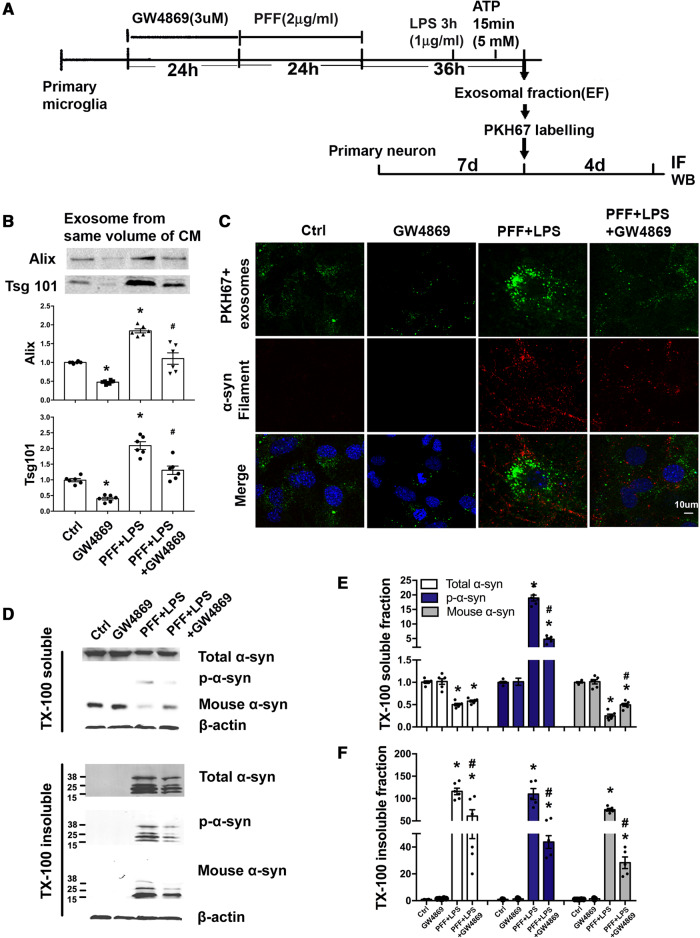
Figure 3.
GW4869 suppresses secretion of microglial exosomes and transmission of α-syn to neurons. (A) Schematic diagram illustrating the timeline and experimental procedures. Primary microglia were treated with either GW4869, PFF, or GW4869 first followed by PFF before LPS and ATP. Ctrl = treatment with ATP before collecting exosome; IF = immunofluorescence. (B) The same volume of microglial culture medium from different experimental conditions was extracted for exosomes, whose levels were determined by western blotting using Alix and Tsg101. (C) GW4869 treatment reduced exosome internalization into neurons resulting in less α-syn aggregation. Exosomes isolated from the same volume of microglia culture medium from different experimental conditions were labelled with the dye PKH67. These exosomes were then added to recipient neurons and incubated for 4 days. Neurons were fixed with 4% PFA and α-syn filament staining was performed. (D–F) Quantitative data and representative immunoblots of TX-100 soluble and insoluble α-syn in recipient neurons. *P < 0.05 versus Ctrl, #P < 0.05 versus PFF+LPS. Data represent mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls post hoc test, n = 3–6 independent experiments.