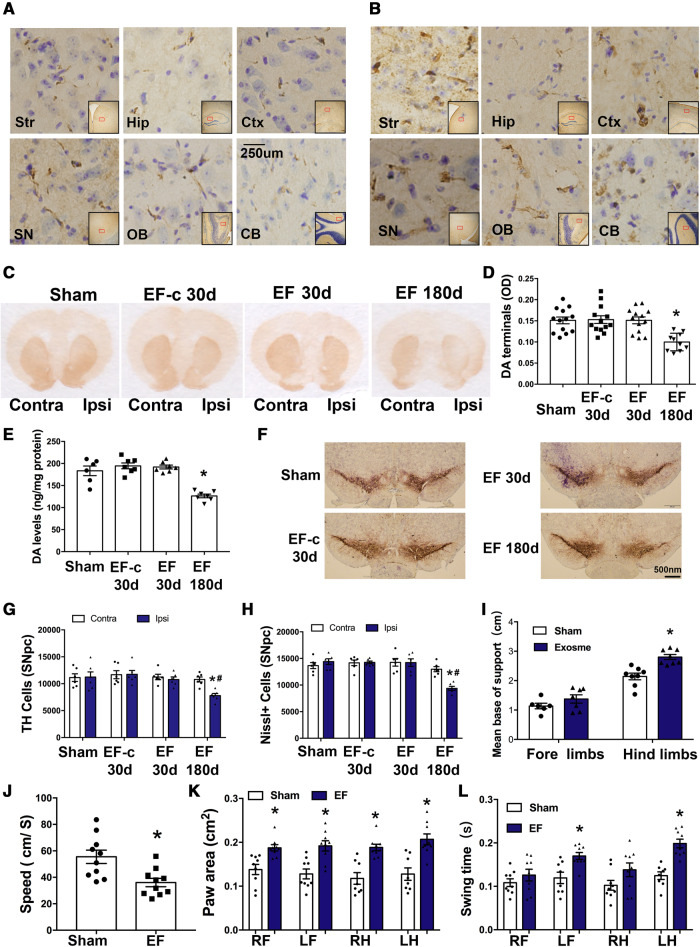
Figure 5.
Exosomes derived from PFF-treated microglia induces α-syn transmission, dopaminergic neuron degeneration and behavioural changes. (A and B) Mice were stereotaxically injected with EF into the right dorsal striatum. Representative images show accumulation of p-α-syn (brown) in different ipsilateral regions at 30 days (A) or 180 days (B) after the injection. (C–E) Striatal dopamine terminals and total dopamine levels were measured at either 30 days or 180 days after injection. The OD level of dopamine terminals (D) showed a 40% decrease and total dopamine levels (E) showed ∼30–35% decrease in hemisphere ipsilateral to injection. Data represent mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls post hoc test, *P < 0.05 versus Sham. (F–H) TH-immunostaining and stereological cell counting of TH-immunoreactive neurons and Nissl-positive neurons in the SNpc. Approximately 33% of TH cells were lost at 180 days in hemisphere ipsilateral to injection. Data represent mean ± SEM, two-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls post hoc test *P < 0.05 versus Sham, #P < 0.05 versus contralateral side. (I–L) Gait analysis was performed 180 days after injection to evaluate locomotor activities. Results were analysed with independent t-test, *P < 0.05 versus Sham. n = 6–8 mice/group. Sham = mice were injected with same volume of D-PBS; EF-c = exosomes from D-PBS treated microglia (control exosome); and EF = exosomes from PFF treated microglia. CB = cerebellum; Contra = contralateral side; Ctx = cortex; Hip = hippocampus; Ipsi = ipsilateral side; LF = left forelimb; LH = left hindlimb; OB = olfactory bulb; RF = right forelimb; RH = right hindlimb; SN = substantia nigra; Str = striatum.