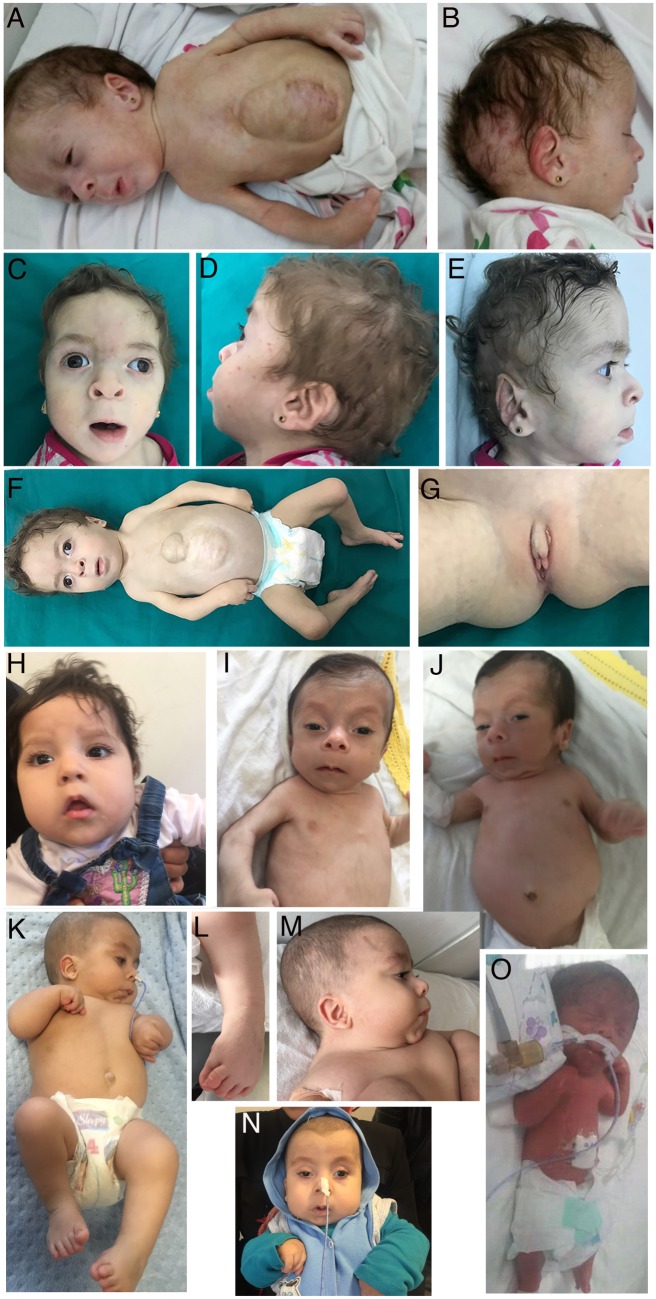
Figure 2.
Clinical features of the patients. (A–G) Case 4 (Patient B-IV:4). (A) Total view of the proband at the age of 9 months, showing multiple contractures at different joints, and corrected omphalocele. (B) Haemangiomas at the right ear and scalp. (C) Dysmorphic facial features of the index patient, at the age of 2 years. Note hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissure, broad nasal bridge with anteverted nares, smooth philtrum and thin upper lip vermilion. (D and E) Lateral view of the patient. Note flat facies, microretrognathia and abnormal asymmetric shaped ears. (F) Total view of the proband showing multiple contractures at different joints, right talipes equinovarus (TEV) and corrected omphalocele with incisional hernia. (G) Abnormal external genitalia with hyperplastic clitoris and hypoplasia of both labia majora and minora. (H) Frontal view of Case 7 (Patient D-V:2) showing low set ears, broad nasal bridge, mild hypertelorism and thin upper lip. (I–O) Cases 9 and 10 (Patients E-III:2 and E-III:1). Photographs of Patient E-III:2 at the age of 3.5 months (I and J) and 15 months (K–N). (I, J, M and N) Note facial dysmorphism (high arched eyebrows, up-slanting palpebral fissures, hypertelorism, depressed nasal bridge, anteverted nares, low set ears, microretrognathia, long philtrum, sparse eyebrows and hair). (I–J) Cervical and axillar web. (J) Abdominal distension. (K–N) Flexion contractures of extremities and (L) pes equinovarus deformity. (O) Case 10 (Patient E-III:1). Note prematurity (born at 29 weeks age of gestation), hypertelorism, macrocephaly, narrow thorax and short limbs.