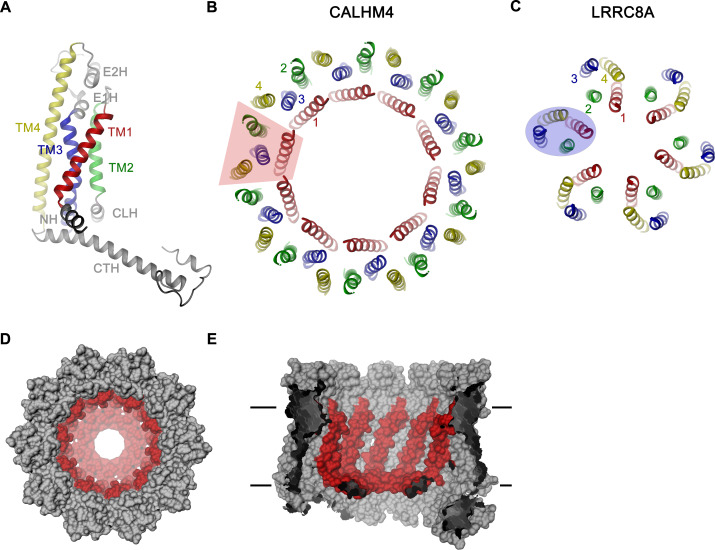
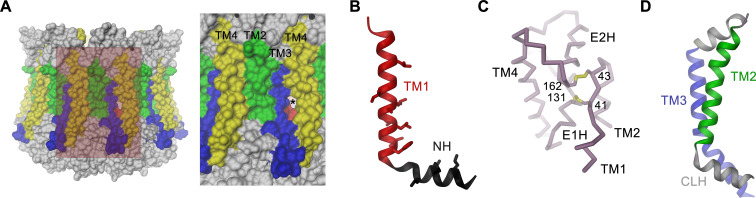
Figure 5. CALHM4 subunit and oligomeric arrangement.
(A) Ribbon representation of the CALHM4 subunit. Secondary structure elements are labeled and transmembrane α-helices are shown in unique colors. View of the transmembrane α-helices of (B), the CALHM4 decamer and (C), the volume regulated anion channel LRRC8A from the extracellular side. B-C, color code is as in A, transmembrane segments of one subunit are numbered. The general shape of a single subunit is indicated (B, trapezoid, C, oval). (D) Surface representation of the CALHM4 decamer. The view is from the outside. (E), Slice through the CALHM4 pore viewed from within the membrane. D, E, TM1 and the N-terminal α-helix NH are colored in red.