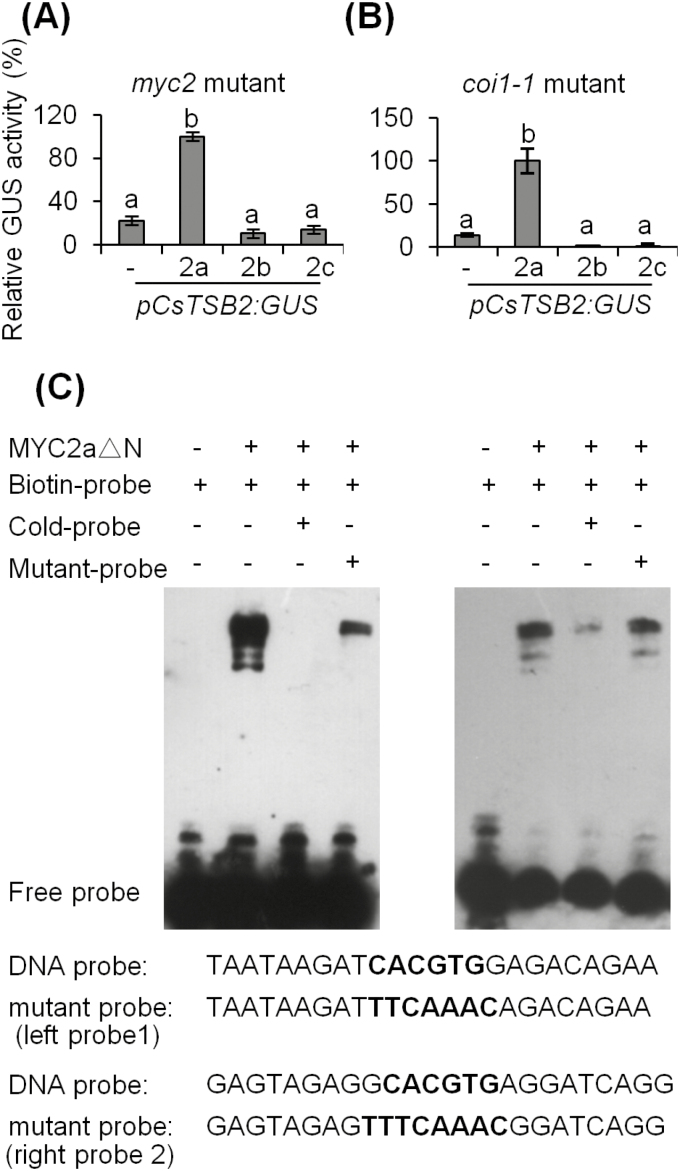
Fig. 5.
Effect of CsMYC2a on CsTSB2 expression. (A) Transient transactivation assays showing that CsMYC2a can activate CsTSB2 expression in the Arabidopsis myc2 mutant mesophyll protoplast. 35S:LUC was used as an internal control. 2a, CsMYC2a; 2b, CsMYC2b; 2c, CsMYC2c. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences (one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s multiple test, P≤0.05). All data are means of three independent experiments, and error bars represent ±SD. (B) Transient transactivation assays showing that CsMYC2a can activate CsTSB2 expression in Arabidopsis coi1-1 mutant mesophyll protoplast. 35S:LUC was used as an internal control. 2a, CsMYC2a; 2b, CsMYC2b; 2c, CsMYC2c. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences (one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s multiple test, P≤0.05). All data are means of three independent experiments, and error bars represent ±SD. (C) Binding of MYC2a protein to the CsTSB2 promoter on EMSA. Two biotin-labeled CsTSB2 promoter fragments containing the wild-type G-box were used as probes. Probe 1 is located at 1482–1459 bp upstream from the ATG initiation codon. Probe 2 is located at 1191–1168 bp from the ATG initiation codon. The unlabeled fragment (100-fold excess) or the fragment with a mutant G-box (100-fold excess) were used as competitors. −, absence; +, presence. The probe sequence is shown below the EMSA image, with the wild-type and mutant G-box in bold letters.