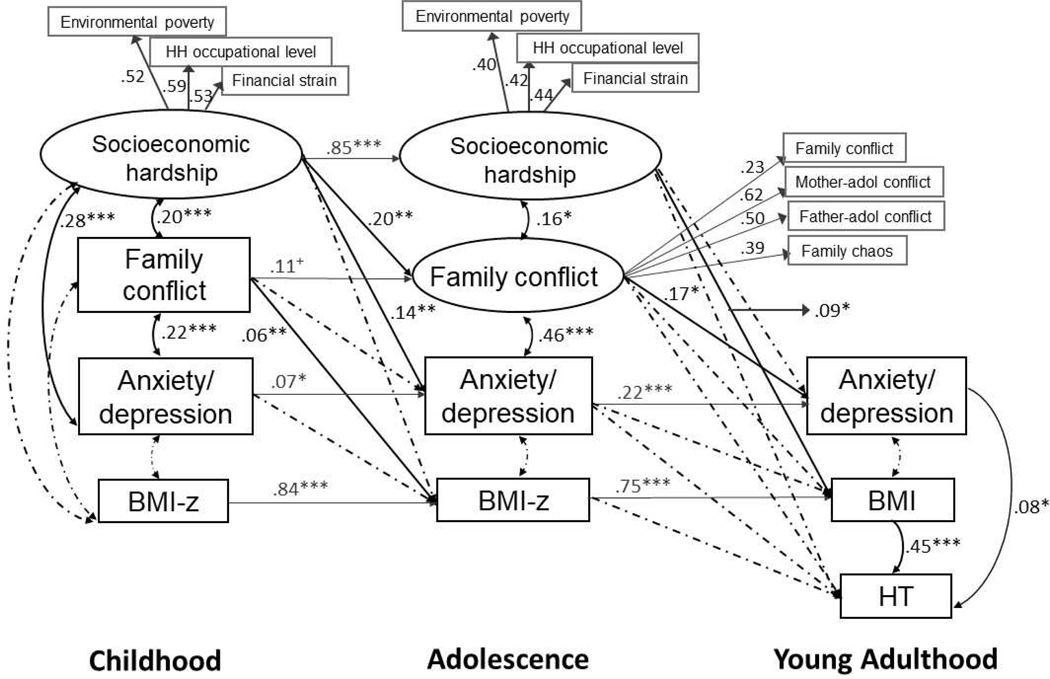
Figure 1.
Model of the across-time associations among socioeconomic hardship, family conflict, anxiety-depression, body mass index (BMI), and hypertension (HT). Standardized coefficients are shown. Nonsignificant paths (shown as dashed lines) were included in the model. Within-time paths at adolescence were included but are not shown for sake of clarity; those not shown were nonsignificant. Model fit was: χ2 (156) = 340.53, CFI = .942, RMSEA = .034, SRMR = .038. N = 1,039. Analyses adjusted for sex, age, parent history of HT, and smoking status at young adulthood. +P < .06. *P < .05. **P < .01. ***P < .001.