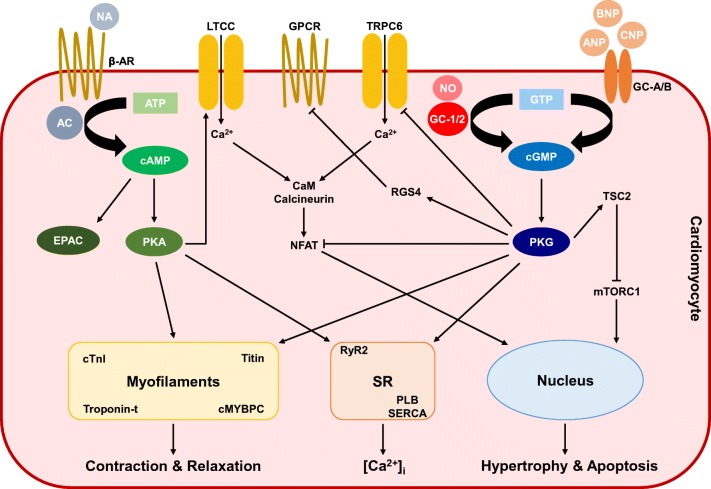
Fig. 1.
Cyclic nucleotide signalling within cardiomyocytes. Cyclic adenosine-3′,5′-monophosphate (cAMP) is synthesised from adenosine-5′-triphosphate (ATP) by the action of adenylyl cyclases (ACs) in response to noradrenaline (NA). Cyclic guanosine-3′,5′-monophosphate (cGMP) is synthesised from guanosine-5′-triphosphate (GTP) by the action of guanylyl cyclases (GCs). GC-1/2 is stimulated by nitric oxide (NO) and is primarily located within the cytosol. Transmembrane GC-A is activated by atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), and GC-B is triggered by C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP). cAMP and cGMP act predominantly via activation of protein kinase A (PKA) and protein kinase G (PKG), respectfully. cAMP also binds exchange protein activated by cAMP (EPAC). Both PKA and PKG phosphorylate multiple cardiomyocyte proteins to effect changes in chronotropy, inotropy and lusitropy, as well as cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis. Arrows indicate stimulation. Blunt lines indicate inhibition. Abbreviations: [Ca2+]i, intracellular concentration of calcium; β-AR, beta-adrenergic receptor; Ca2+, calcium; CaM, calmodulin; cMYBPC, cardiac myosin–binding protein C; cTnI, cardiac troponin I; GPCR, G protein–coupled receptor; LTCC, L-type calcium channel; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; NP, natriuretic peptide; PLB, phospholamban; RGS, regulator of G protein signalling; RyR2, ryanodine receptor; SERCA, sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase; SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum; TRPC, transient receptor potential cation channel; TSC2, tuberin