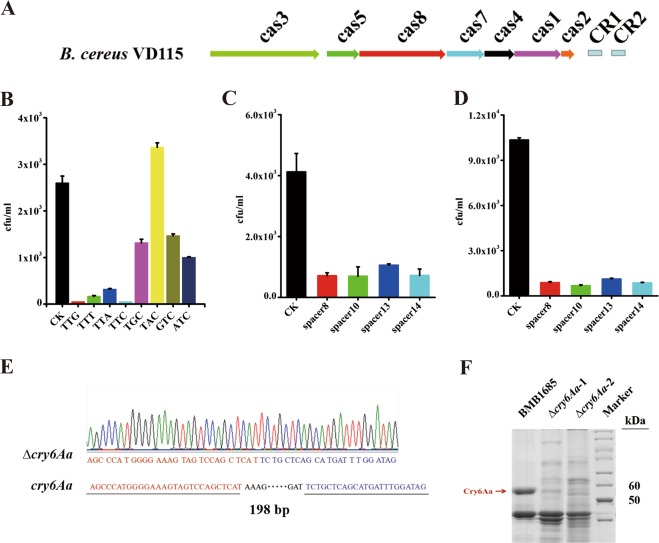
Fig. 6. Functional analysis of the subtype I-C CRISPR-Cas system from B. cereus strain VD115.
a The genetic organization of cas operon in subtype I-C CRISPR-Cas system loci from B. cereus VD115. b Plasmids derivatives of pHT-304 containing synthetic VD115 spacer 1 accompanied by 5′-TTN or 5′-NNN PAMs (TGC, TAC, GTC and ATC) were transformed into B. cereus VD115 strain and the transformation efficiency of plasmids was analyzed and showed as the number of CFU/mL. The immunity assays of subtype I-C CRISPR-Cas locus in B. cereus VD115 (c) and in B. thuringiensis BMB1685 (d) strains. The immunity was assessed via transformation of plasmids containing spacers flanked by a 5′-TTC PAM site in both strains. The transformation was conducted via electroporation, and the results were expressed as the number of CFU/mL. The pHT-304 vector was used as negative control in all assays. e T-A cloning and sequencing demonstrated the deletion region of cry6Aa gene. A loss of 198 bps in the edited cry6A (∆cry6Aa) is shown, compared with the wild type cry6Aa gene in BMB1685 strain. f The Cry6Aa protein production in BMB1685 strain and in selected cry6Aa deletion mutants was analyzed by SDS-PAGE. The red arrow points to the band of the complete Cry6Aa protein.