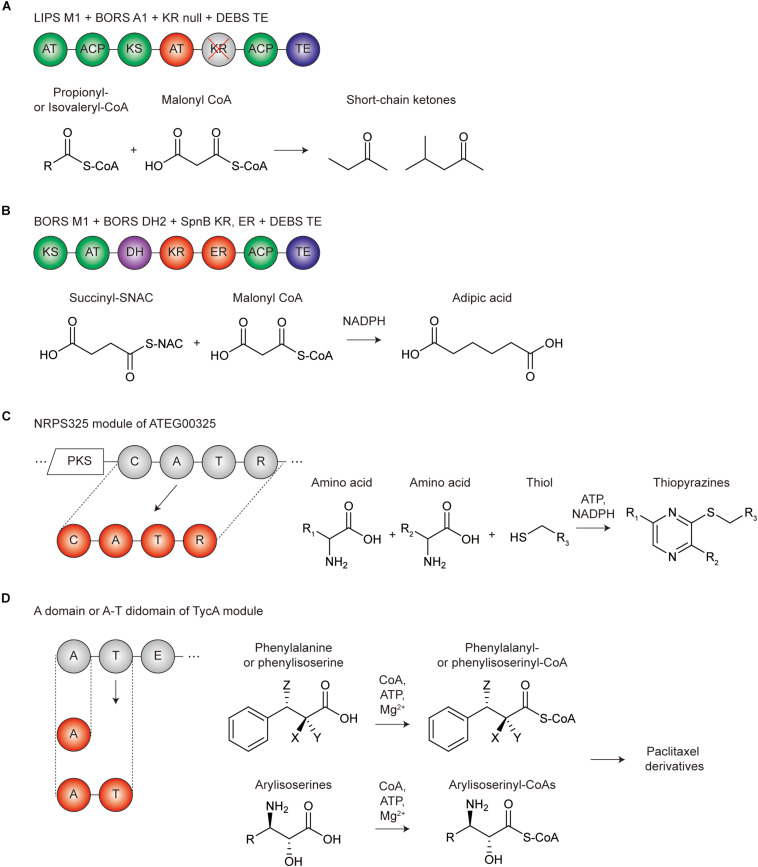
FIGURE 4.
Representative repurposing examples of modular PKS and NRPS for de novo biosynthetic pathways. (A) Repurposing the PKS domains and modules for the production of short-chain ketones. Green circles are the domains in module 1 of β-lipomycin PKS (LIPS M1), red circles are the AT domains in module 1 of borrelidin PKS (BORS A1), gray circles with the red crossed line are the inactivated KR domain (KR null), and the blue circles are the TE domain of DEBS PKS. (B) Repurposing the PKS domains and modules for the production of adipic acid. Green circles are the domains in module 1 of borrelidin PKS (BORS M1), red circles are the KR and ER domain in SpnB module of spinosyn PKS (SpnB KR, ER), and the blue circles are the TE domain of DEBS PKS. (C) Repurposing the NRPS module for the production of thiopyrazines. NRPS325 module of ATEG00325 PKS-NRPS hybrid megasynthetase was isolated (red circles) to promote the reaction for the thiopyrazine production itself. (D) Repurposing the NRPS domain for the production of paclitaxel derivatives. The A or A-T didomain in TycA module of tyrocidine A PKS was isolated (red circles) to be repurposed for the production of phenylalanyl-, phenylisoserinyl-, arylisoserinyl-CoAs, which are the precursors of the paclitaxel derivatives; X, NH2 or H; Y, H or OH; Z, NH2 or H.