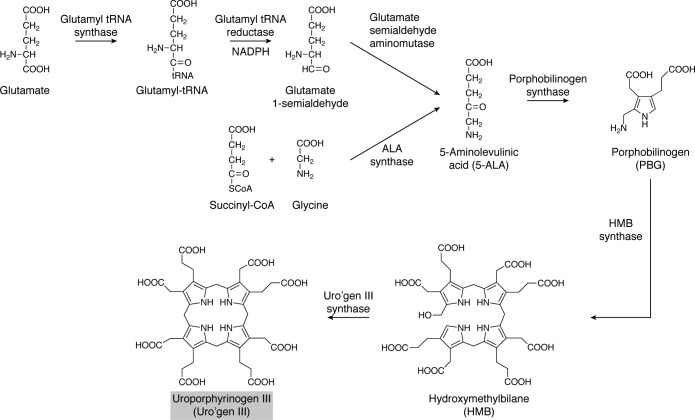
Figure 2.
The two routes for the biosynthesis of 5-ALA and the subsequent biosynthesis of uroporphyrinogen III. The Shemin, or C4, route involves the condensation of glycine and succinyl-CoA and is mediated by the enzyme 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase. The C5 pathway acquires the intact carbon skeleton from glutamate and utilizes glutamyl-tRNA as an intermediate. The glutamyl-tRNA undergoes a reduction by glutamyl-tRNA reductase to give GSA. The final step involves the enzyme GsaM, which rearranges the GSA into 5-ALA. Then two molecules of 5-ALA are condensed into PBG by the action of the enzyme porphobilinogen synthase. Next, four molecules of PBG are deaminated and linked together to give a linear bilane called HMB in a reaction catalyzed by HMB synthase. The final step involves the cyclization and inversion of the terminal D ring to give uroporphyrinogen III. The gray box for uroporphyrinogen III also identifies this central intermediate in Figs. 3 and 14.