Figure 2.
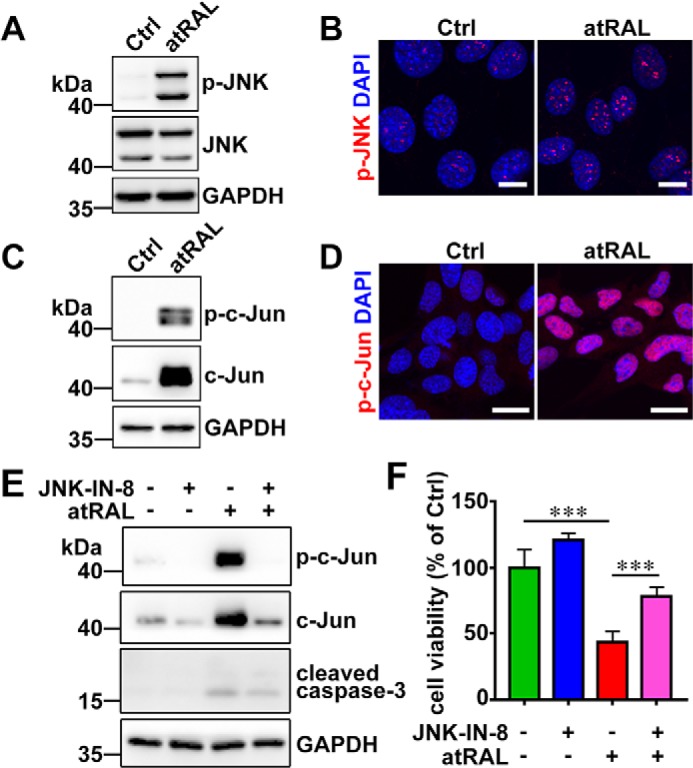
atRAL activates JNK signaling in 661W photoreceptor cells. A, immunoblot analysis of p-JNK and JNK in lysates of 661W photoreceptor cells treated with 5 μm atRAL or vehicle (DMSO) alone for 6 h. GAPDH was used as an internal control. Molecular mass markers (kDa) are indicated to the left of the blots. Ctrl, control. B, immunofluorescence staining for p-JNK in 661W photoreceptor cells incubated with 5 μm atRAL or vehicle (DMSO) alone for 6 h. Nuclei were stained blue with DAPI. Scale bars, 10 μm. C, Western blot analysis of p-c-Jun and c-Jun in lysates of 661W photoreceptor cells exposed to 5 μm atRAL or vehicle (DMSO) alone for 6 h. GAPDH was used as an internal control. D, immunofluorescence staining for p-c-Jun in 661W photoreceptor cells exposed to 5 μm atRAL or vehicle (DMSO) alone for 6 h. Nuclei were stained blue with DAPI. Scale bars, 10 μm. E, immunoblot analysis of p-c-Jun, c-Jun, and cleaved caspase-3 in 661W photoreceptor cells treated with 5 μm atRAL for 6 h in the absence or presence of 1 μm JNK-specific inhibitor JNK–IN-8. Note that cells were pretreated with 1 μm JNK–IN-8 for 1 h. Cells treated with vehicle (DMSO) or JNK–IN-8 served as controls. GAPDH was utilized as an internal control. F, cell viability was detected by MTS assay. 661W photoreceptor cells were pretreated with JNK-specific inhibitor JNK–IN-8 (1 μm) for 1 h, followed by incubation with and without 5 μm atRAL for 6 h. Control cells were treated with atRAL or vehicle (DMSO) alone. Each value represents mean ± S.D. (error bars) of three independent experiments, and statistical analyses were performed by using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-test.
