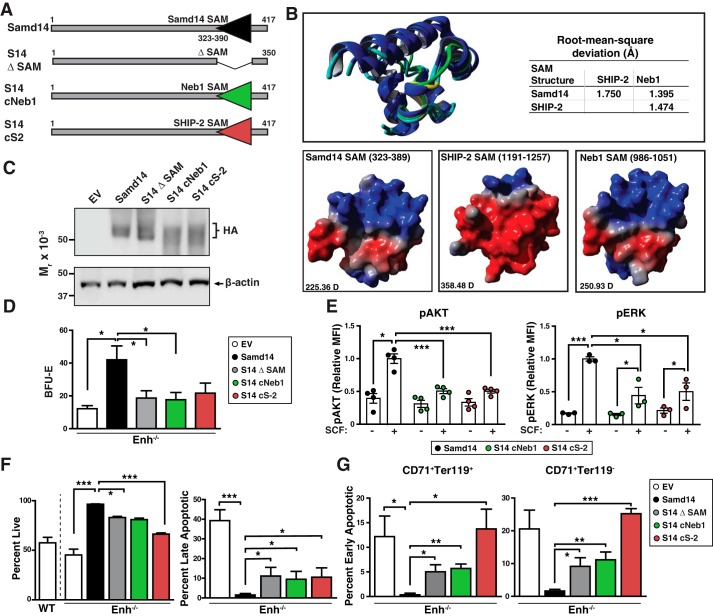
Figure 6.
Dissecting Samd14 SAM domain function with chimeric SAM domain proteins. A, schematic representation of fusion constructs. B, top, overlay of predicted SAM domains of Samd14 and Neb1 with SHIP-2. Blue, α helix; teal, coil; green, bend; and yellow, turn. Bottom, surface models of Samd14, SHIP-2, and Neb1 SAM domains. Red, negatively charged area; blue, positive; gray, neutral. D, dipole/debye. C, Western blotting of spleen progenitors retrovirally-infected with EV, HA-tagged Samd14, a SAM domain-deleted mutant of Samd14 (Samd14 ΔSAM), and Samd14 with SAM domain sequence of Neurabin-1 (S14–cNeb1) and Samd14 with SAM domain sequence of SHIP-2 (S14-cS2). D, quantitation of BFU-E colonies from 12-h cultured GFP+ cells (n = 7, BFU-E numbers normalized to colonies per 3 × 104 GFP+ cells). E, quantitation of pAKT and pERK1/2 median fluorescence intensity post-stimulation with SCF (10 ng/ml). (n = 4 for each condition). F, quantitation of flow cytometric analysis of noncell membrane permeating DNA dye (Draq7) and anti-annexin V Pacific Blue (AnnV). Cells were first segregated based on GFP+, CD71+, and Ter119+. Draq7−AnnV−, live; and Draq7+AnnV+, late apoptotic. G, quantitation of flow cytometric analysis of noncell membrane permeating DNA dye (Draq7) and anti-annexin V Pacific Blue (AnnV). Left, cells were segregated based on GFP+, CD71+, and Ter119+. Right, cells were segregated based on GFP+, CD71+, and Ter119−. Draq7−AnnV+, early apoptotic (n = 3). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (S.E.). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 (two-tailed unpaired Student's t test).