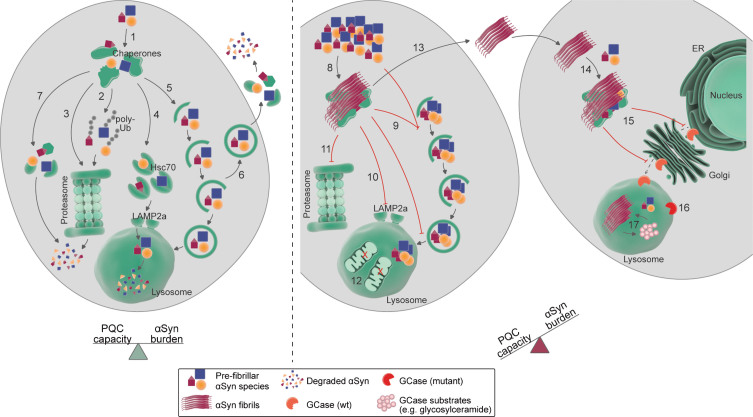
Fig. 2.
Targeting and processing of alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) by protein quality control (PQC) pathways. Left: in normal conditions, in which the cellular PQC capacity is in balance with the α-Syn burden, soluble as wells as pre-fibrillar α-Syn assemblies (after disassembly) have been shown to be targeted to and degraded by several PQC components. The initial survey of α-Syn species might be performed by molecular chaperones (1), which can facilitate the sorting of α-Syn to distinct degradative routes, such as the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS; 2), a ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation pathway (3), chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA; 4), macroautophagy (5), secretion via endosomes (6) [162], and proteolytic digestion by intracellular (7) or extracellular proteases. Right: in aged organisms or pathological conditions, the α-Syn burden surpasses the cellular PQC capacity, leading to α-Syn accumulation and subsequent aggregation. Fibrillar α-Syn assemblies can trap several biomolecules, including molecular chaperones (8), which contributes to chaperone depletion and decreases PQC capacity. Similarly, α-Syn aggregation has been linked to impairment of different steps of macroautophagy (9), CMA (10), and proteasomal degradation (11). In some experimental setups, increased α-Syn levels can also lead to increased autophagic flux and destruction of organelles, such as mitochondria (12). α-Syn species can also be secreted to the extracellular space and taken up by neighboring cells (13), where they seed the aggregation of soluble α-Syn species (14). α-Syn aggregation additionally impairs the intracellular trafficking of other proteins, such as the lysosomal enzyme glucocerebrosidase (GCase; 15). Decreased lysosomal GCase activity, due to either mislocalization of wildtype (wt) GCase or mutant GCase variants (16), leads to accumulation of GCase substrates (such as glycosylceramide; 17), which might potentiate α-Syn aggregation. See main text for further mechanistic details and references. ER: endoplasmic reticulum; Hsc70: heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein; LAMP2a: lysosome-associated membrane protein 2 isoform a; poly-Ub: poly-ubiquitin.