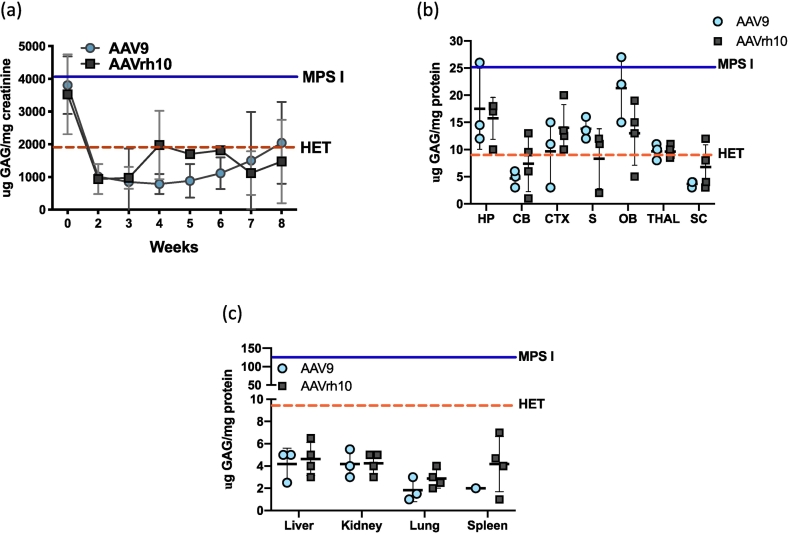
Fig. 4.
Glycosaminoglycan storage materials in tissues and in urine post-AAV administration. (A) GAG excretion in urine. Urine was collected at 1 to 2-week intervals and assayed for glycosaminoglycans. The levels of GAGs found in untreated MPS I mice ranged from 4000 to 6000 μGAG/mg creatinine and in normal heterozygotes ranged from 300 to 2000 μGAG/mg creatinine, and are indicated by solid and dashed horizontal lines, respectively. Bars represent means +/− SD. (B). GAG accumulation in brain. Tissue lysates from different parts of the brain were assayed for GAG storage. GAG levels were normalized in the cerebellum and spinal cord and reduced in other parts of the brain from treated animals. The levels of GAG found in untreated MPS I mice ranged from 15-25 μg GAG/mg protein in the brain, and in normal heterozygotes ranged from 1-10 μg GAG/mg protein, and are indicated by solid and dashed horizontal lines, respectively. Mean +/− SD values are represented by bold horizontal lines and light vertical lines respectively. HP, hippocampus; CB, cerebellum; CTX, cortex; S, striatum; OB, olfactory bulb; THAL, thalamus; SC, spinal cord. (C) GAG accumulation in peripheral organs. Lysates from peripheral tissues showed normalization of GAG levels. The levels of GAG found in untreated MPS I mice ranged from 50-150 μg GAG/mg protein and are indicated by the solid horizontal line. Normal heterozygote levels range from 1-10 μg GAG/mg protein, and are indicated by a dashed horizontal line. Mean +/− SD values are indicated.