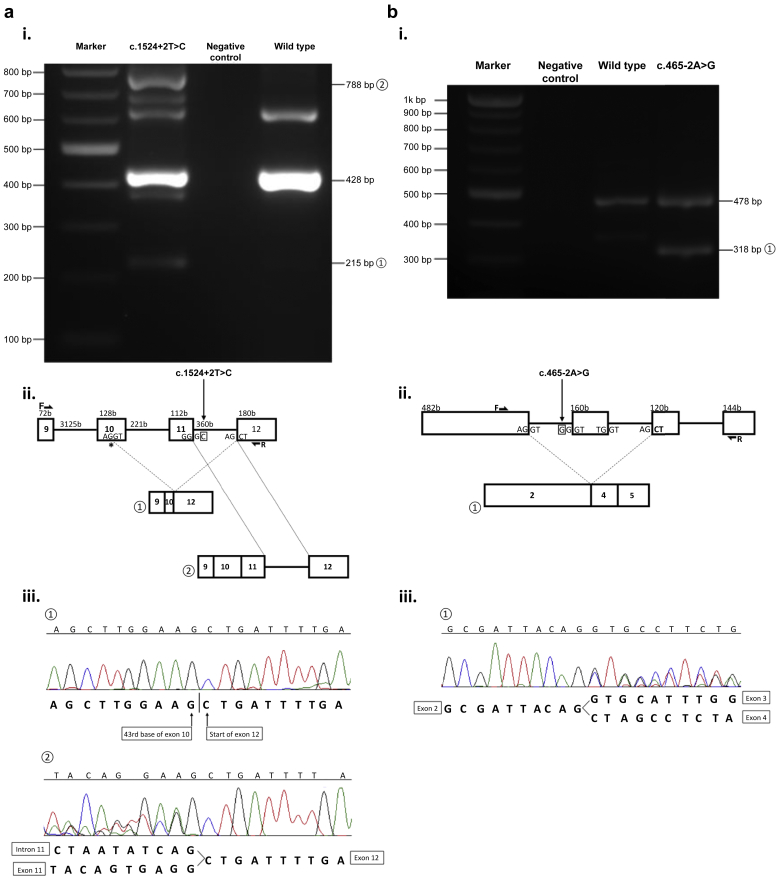
Figure 4.
DGKE RNA studies. PCR, gel electrophoresis, and sequence analysis of cDNA reverse transcribed from peripheral blood lymphocytes were performed and demonstrated abnormal splicing for both c.1524+2T>C and c.465-2A>G. (a) NCL36: c.1524+2T>C. Three transcripts were detected on sequencing and are labeled on the (i) gel and (ii) diagram: wild type (428 bp); splice variant ① (215 bp): this corresponds to the first 43 bases of exon 10 spliced to exon 12 because of a cryptic splice site (∗) in exon 10; splice variant ② (788 bp): this represents a gain of 360 bp that corresponds to the inclusion of the whole of intron 11. The Sanger sequencing traces are shown in (iii). The other PCR products visible on the gel were of insufficient intensity to be adequately sequenced. (b) NCL30 and NCL39: c.465-2A>G. Two transcripts were detected and shown on the (i) gel and (ii) diagram: wild type (478 bp) and an abnormal transcript ①; at 318 bp, this represents a deletion of 160 bp that corresponds to the whole of exon 3. The Sanger sequencing trace is shown in (iii). The positions of forward (F) and reverse (R) primers are shown. Details of the primer design are available in Supplementary Figure S6.