Figure 6.
Stromal-Immune Crosstalk Supports the Development of an Immunosuppressive Niche
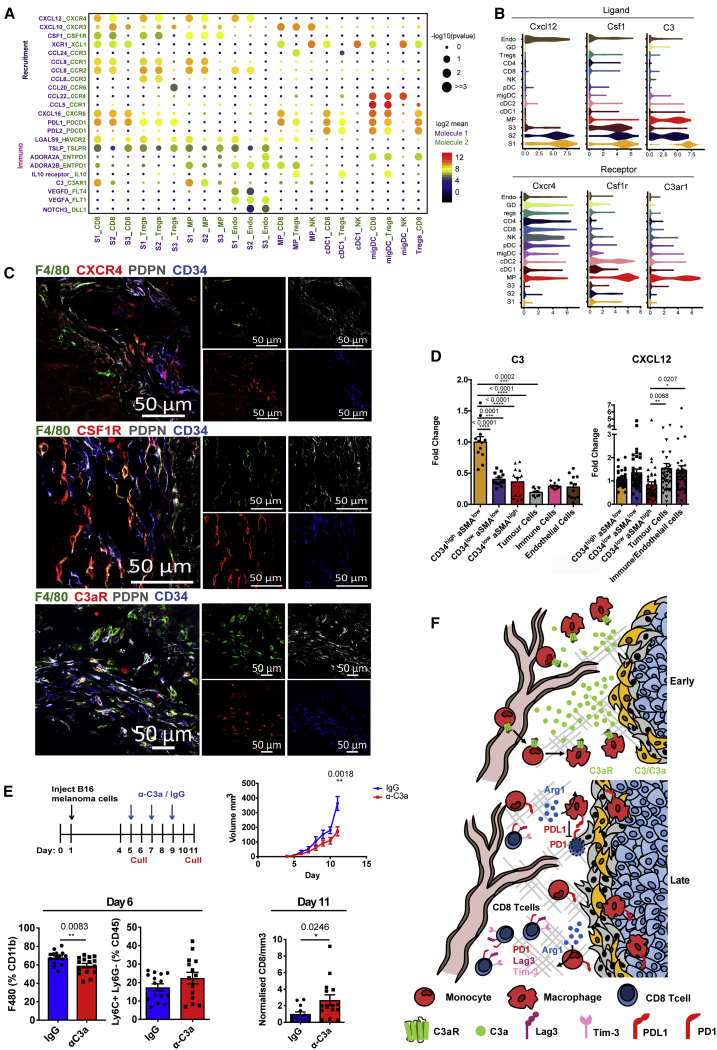
(A) Overview of selected statistically significant interactions between stromal subsets and other cell types using a cell-cell communication pipeline based on CellPhoneDB. Size indicates p values (permutation test, see STAR Methods), and color indicates the means of the receptor-ligand pairs between 2 clusters.
(B) Violin plots displaying expression log(TPM+1) of ligands Cxcl12, Csf1, and C3 and cognate receptors Cxcr4, Csf1r, and C3ar1 on respective stromal populations. n = 26 mice.
(C) Confocal images of representative tumor-tissue borders. CXCR4, CSFR1, or C3aR expressing macrophages located proximally to CD34+ CAFs (green, F4/80; red, CXCR4, CSF1R, or C3aR; white, PDPN; blue, CD34). Scale bars, 50 μm.
(D) Flow cytometric quantification of CXCL12 and C3 expression across compartments of the tumor microenvironment. Each point represents a tumor. CXCL12 n = 42 tumors, C3 n = 12 tumors. One-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test.
(E) In vivo blockade of C3a in established tumors. Top left: experimental design and treatment regimen; top right: tumor volume (in cubic millimeters) of mice treated with IgG control (blue) or anti-C3a (red); bottom left: myeloid infiltration in day 6 tumors, after 24 h of treatment with IgG or anti-C3a. The number of F4/80 and Ly6C+ Ly6G− cells are shown as a percentage of Cd11b and CD45 cells, respectively; bottom right: the number of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells at day 11, displayed as raw counts normalized to tumor volume (in cubic millimeters). Data presented as means ± SEMs. n = minimum 13 mice. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; t test.
(F) Schematic diagram of the dynamic crosstalk identified within the tumor microenvironment.