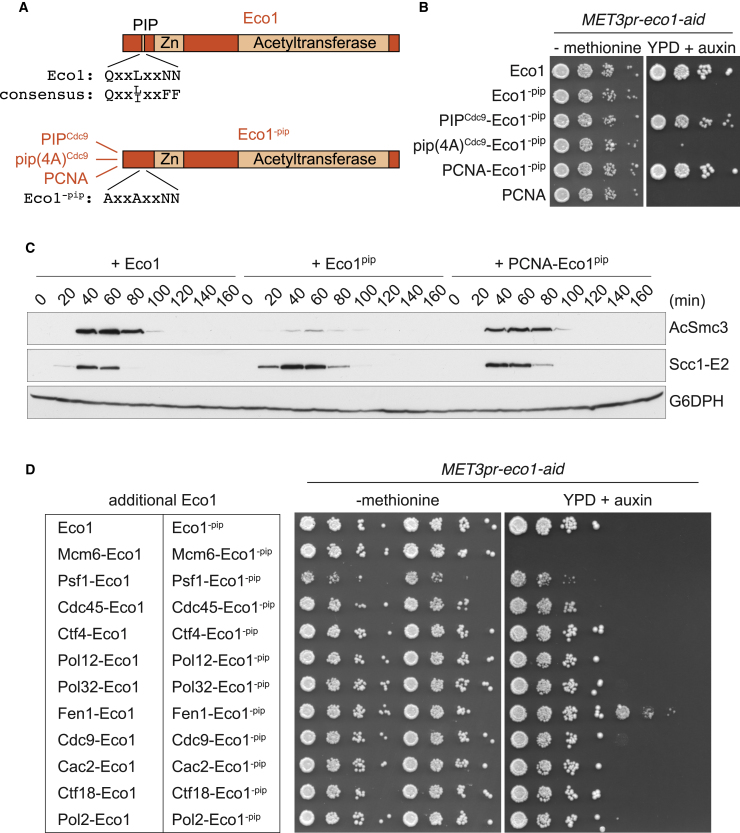
Figure 7.
Eco1 Functions in Concert with PCNA at a Late Stage of Replication
(A) Schematic of Eco1 and its PIP box, as well as the fusion constructs made with the PIP box mutant protein (Eco1-pip).
(B) 10-fold serial dilutions of MET3pr-eco1-aid cultures were spotted on medium lacking methionine or on YPD medium containing auxin to repress Eco1 expression and induce its degradation. The indicated proteins were additionally expressed under control of the Eco1 or PCNA promoters, respectively.
(C) MET3pr-eco1-aid cells expressing the indicated additional proteins were synchronized in G1, depleted of endogenous Eco1, and released into synchronous cell-cycle progression. Smc3 acetylation was analyzed by western blotting. Scc1 served as a marker for cell-cycle progression, and Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) served as the loading control.
(D) 10-fold serial dilutions of MET3pr-eco1-aid cultures that in addition harbored Eco1pip fusions with the indicated proteins at their respective endogenous gene loci were spotted on the indicated media.
See Figure S7 for demonstration that Ctf18 targets cohesin acetylation, for an Eco1-PCNA interaction analysis, and for protein expression levels of the Eco1-pip fusion proteins.