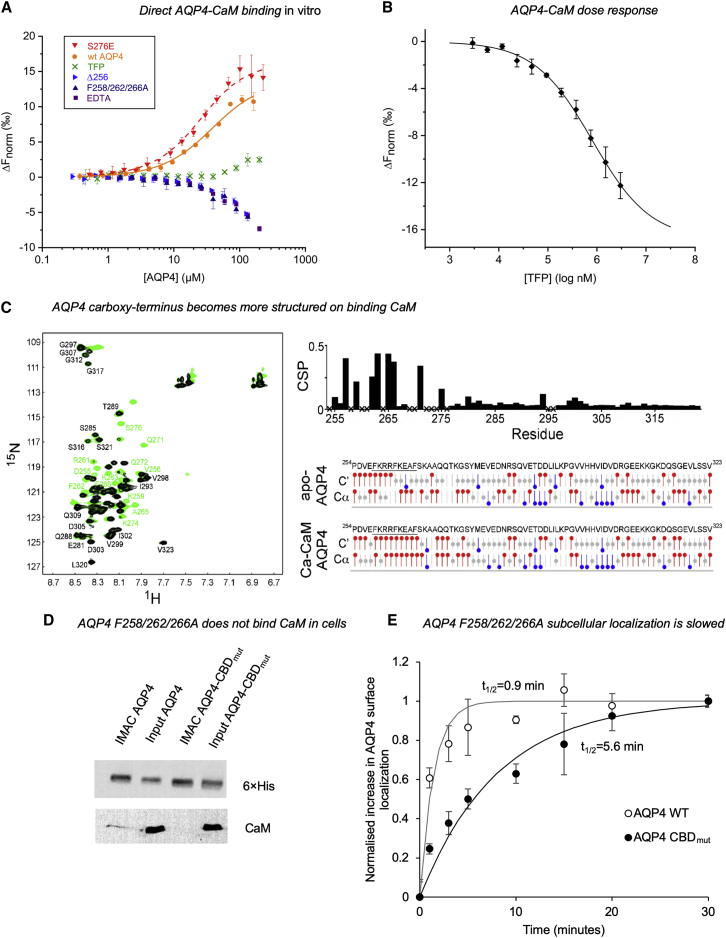
Figure 3.
Binding of CaM to the AQP4 Carboxyl Terminus
(A) Microscale thermophoresis (MST) data showing that full-length AQP4 interacts directly with CaM. The binding curve, obtained by plotting ΔFnorm against [AQP4], could be fitted to a one-to-one binding model (estimated Kd of 29 ± 5.6 μM). Addition of 5 mM EDTA demonstrated that binding was Ca2+ dependent. The interaction was also inhibited by addition of 1 mM TFP. Truncation of the AQP4 carboxyl terminus before the predicted CBD (AQP4-Δ256) resulted in a construct that did not interact with CaM. AQP4 F258/262/266A did not bind CaM. The phospho-mimetic mutant AQP4-S276E bound CaM with approximately 2-fold higher affinity (Kd = 17 ± 3.1 μM) than WT AQP4 (p = 0.031), suggesting that phosphorylation of S276 affects the interaction with CaM.
(B) Response curve showing that TFP inhibits the interaction between AQP4 and CaM in a concentration-dependent manner. The concentration of TFP needed for 50% inhibition (IC50) was estimated to be 790 ± 2 μM.
(C) Left: 1H, 15N-HSQC NMR data showing the interaction of the recombinant carboxyl terminus of AQP4 (recAQP4ct; residues 254–323) with CaM at 30°C. Chemical shift perturbations (CSPs) were observed by titrating CaM into 0.5 mM 13C, 15N-labeled recAQP4ct with 0 (black) and 2 (green) molar equivalents of CaM in the presence of 6 mM Ca2+. Top right: CSPs induced by CaM binding to recAQP4ct were plotted as a function of the residue number (X indicates that data are not available). Bottom right: chemical shift index (CSI) values of the Cα and C′ atoms of recAQPct. The sequence of the CBD is underlined. The region with consecutive positive CSI values (red) represents an α-helical conformation.
(D) Anti-CaM immunoblotting following nickel affinity chromatography (IMAC) from 1% Triton X-100 lysates (input) of HEK293 cells transfected with AQP4-His6 (AQP4) or AQP4 F258/262/266A-His6 (AQP4 CBDmut) demonstrates that the F258A/F262A/F266A mutation abrogates AQP4-CaM binding.
(E) Cell-surface biotinylation followed by neutravidin/anti-AQP4 ELISA demonstrates a reduced rate of AQP4 plasma membrane accumulation in AQP4-transfected HEK293 cells upon F258A/F262A/F266A mutation (AQP4 CBDmut) compared with the wild-type control (AQP-WT). Normalized data were fitted to functions of the form 1−e−kt, and t1/2 was calculated as −ln(0.5)/k.
See also Figures S4 and S5.