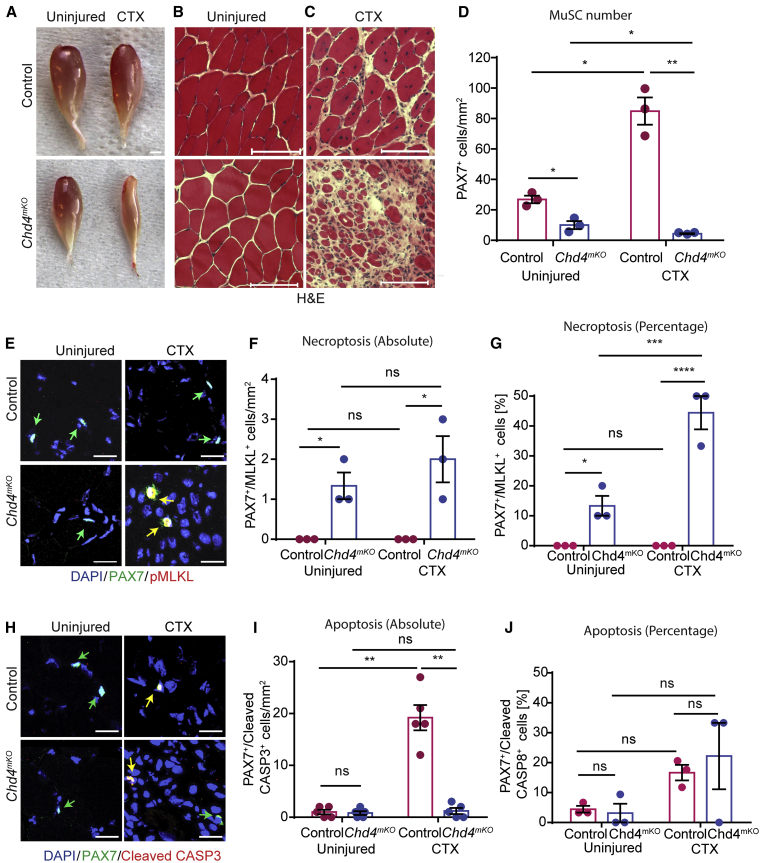
Figure 4.
Chd4 Is Required for Muscle Regeneration and Suppresses Necroptosis of MuSCs
(A) Macroscopic images of uninjured and CTX-injured TA muscles from control and Chd4mKO mice.
(B and C) H&E staining of sections of uninjured muscle (B) and injured muscle (C) derived from muscles shown in (A). Scale bar (A–C), 100 μm.
(D) Quantification of PAX7+ cells from control and Chd4mKO muscles using PAX7 antibodies (n = 3 for each group).
(E–J) Immunofluorescence staining of TA muscle sections 2 weeks after CTX injury from control and mdx mice (n = 3 for each group) using antibodies against PAX7 and pMLKL to detect necroptosis (E–G) and PAX7 and cleaved CASP3 (H–J) to detect apoptosis (n = 5 for each group). Scale bar, 25 μm. (F, G, I, and J) Absolute and relative quantification of data represented in (E) and (H) (n = 3–5 for each group).
Statistical analysis: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test with alpha = 5%. All analyses indicated across the experiments were biological replicates unless otherwise stated.