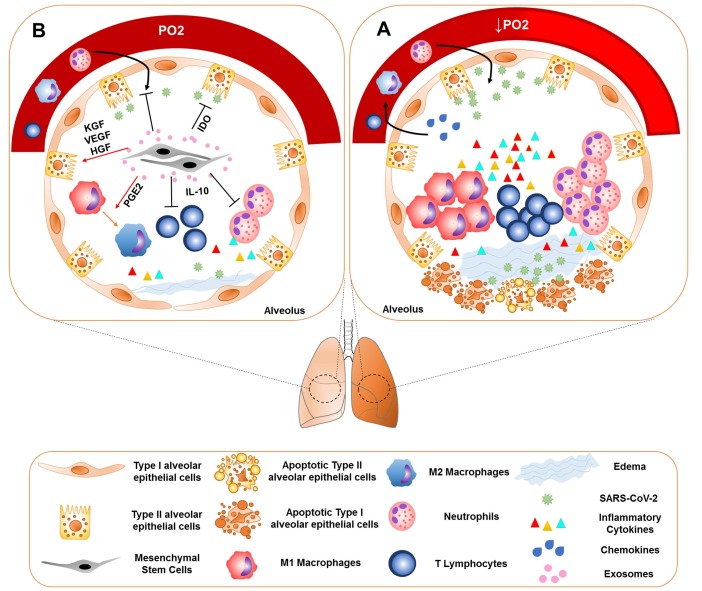
Fig. 1.
Immunopathogenesis of the SARS-CoV-2 and the therapeutic potential of the MSC exosomes. (A) SARS-CoV-2 infects type II alveolar epithelial cells or other target cells, which express ACE2. The influx of neutrophils, monocytes and T cells is induced by secretion of the chemokines. Accumulation of the inflammatory cells leads to the production of large amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines, that is known as cytokine storm. Cytokine storm is the main cause of ARDS in COVID-19. These inflammatory responses may cause the apoptosis of the alveolar cells, lung fibrosis, edema, and organ failure. (B) MSCs and their exosomes suppress inflammation and reduce inflammation-induced lung injury through their immunomodulatory properties. These cells affect the macrophages and alter the phenotype of macrophages from M1 to M2 by releasing PG-E2. MSCs also reduce the production of the inflammatory cytokines and increase IL-10 production. IL-10 reduces neutrophils recruitment to the lungs. MSCs have also the tissue repair potential by producing KGF, VEGF, and HGF. These cells are involved in the pathogen clearance through expressing IDO.