Figure 1.
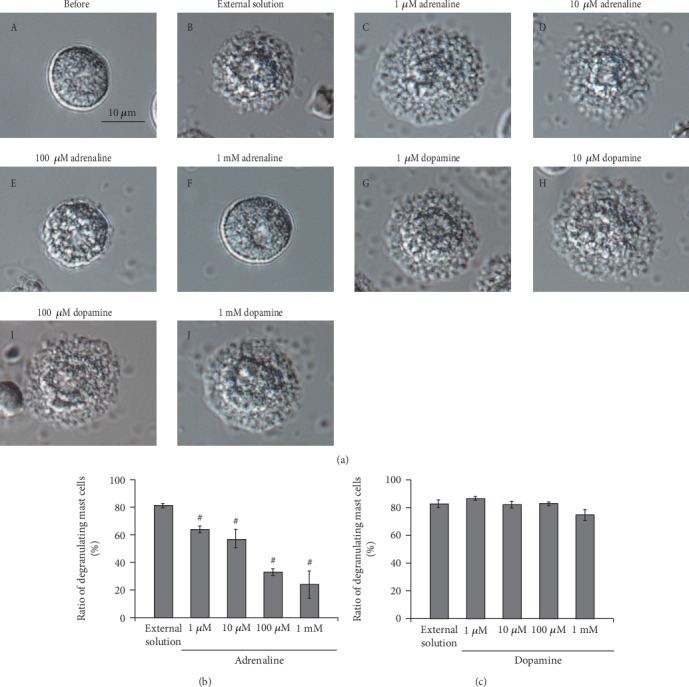
Effects of adrenaline and dopamine on mast cell degranulation. (a) Differential-interference contrast (DIC) microscopic images were taken before (A) and after exocytosis was externally induced by compound 48/80 in mast cells incubated in the external solutions containing no drug (B), 1 μM adrenaline (C), 10 μM adrenaline (D), 100 μM adrenaline (E), 1 mM adrenaline (F), 1 μM dopamine (G), 10 μM dopamine (H), 100 μM dopamine (I), and 1 mM dopamine (J). Effects of different concentrations (1, 10, and 100 μM and 1 mM) of adrenaline (b) and dopamine (c). After the mast cells were incubated in the external solutions containing no drug or either drug, exocytosis was induced by compound 48/80. The numbers of degranulating mast cells were expressed as percentages of the total mast cell numbers in selected bright fields. #p < 0.05 vs. incubation in the external solution alone. Values are means ± SEM. Differences were analyzed by ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test.
